Note
Click here to download the full example code
Discipline¶
from __future__ import division, unicode_literals
from numpy import array
from gemseo.api import (
configure_logger,
create_discipline,
generate_coupling_graph,
generate_n2_plot,
get_all_inputs,
get_all_outputs,
get_available_disciplines,
get_discipline_inputs_schema,
get_discipline_options_defaults,
get_discipline_options_schema,
get_discipline_outputs_schema,
)
from gemseo.core.discipline import MDODiscipline
configure_logger()
Out:
<RootLogger root (INFO)>
In this example, we will discover the different functions of the API
related to disciplines, which are the GEMSEO’ objects
dedicated to the representation of an input-output process. All classes
implementing disciplines inherit from MDODiscipline which is an
abstract class.
Get available disciplines¶
The get_available_disciplines() function
can list the available disciplines:
get_available_disciplines()
Out:
['Aerodynamics', 'AnalyticDiscipline', 'AutoPyDiscipline', 'BurgersDiscipline', 'ConcatenationDiscipline', 'ConstrAggegationDisc', 'DOEScenario', 'DiscFromExe', 'FilteringDiscipline', 'LinearDiscipline', 'MDOAdditiveChain', 'MDOChain', 'MDOObjScenarioAdapter', 'MDOParallelChain', 'MDOScenario', 'MDOScenarioAdapter', 'MatlabDiscipline', 'Mission', 'PropaneComb1', 'PropaneComb2', 'PropaneComb3', 'PropaneReaction', 'RosenMF', 'ScalableDiscipline', 'Scenario', 'Sellar1', 'Sellar2', 'SellarSystem', 'SobieskiAerodynamics', 'SobieskiAerodynamicsSG', 'SobieskiBaseWrapper', 'SobieskiBaseWrapperSimpleGram', 'SobieskiChain', 'SobieskiMDAGaussSeidel', 'SobieskiMDAJacobi', 'SobieskiMission', 'SobieskiMissionSG', 'SobieskiPropulsion', 'SobieskiPropulsionSG', 'SobieskiStructure', 'SobieskiStructureSG', 'Structure', 'SurrogateDiscipline', 'TMDiscipline', 'TMMainDiscipline', 'TMSubDiscipline', 'XLSDiscipline']
Create a discipline¶
The create_discipline() function can create a
MDODiscipline or a list of MDODiscipline
by using its class name. Specific **options can be provided in
argument. E.g.
disciplines = create_discipline(
[
"SobieskiPropulsion",
"SobieskiAerodynamics",
"SobieskiMission",
"SobieskiStructure",
]
)
print(type(disciplines))
print(type(disciplines[0]))
print(isinstance(disciplines[0], MDODiscipline))
Out:
<class 'list'>
<class 'gemseo.problems.sobieski.wrappers.SobieskiPropulsion'>
True
This function can also be used to create a particular MDODiscipline
from scratch, such as AnalyticDiscipline
or AutoPyDiscipline. E.g.
addition = create_discipline("AnalyticDiscipline", expressions_dict={"y": "x1+x2"})
print(addition.execute({"x1": array([1.0]), "x2": array([2.0])}))
Out:
{'x1': array([1.]), 'x2': array([2.]), 'y': array([3.])}
Get all inputs/outputs¶
The get_all_inputs() function can list all the inputs
of a list of disciplines, including the sub-disciplines if the
argument recursive (default: False) is True,
merging the input data from the discipline grammars. E.g.
print(get_all_inputs(disciplines))
Out:
['y_31', 'y_32', 'y_23', 'x_shared', 'y_21', 'y_24', 'y_12', 'y_14', 'x_1', 'x_2', 'x_3', 'y_34']
The get_all_outputs() function can list all the inputs
of a list of disciplines, including the sub-disciplines if the
argument recursive (default: False) is True,
merging the input data from the discipline grammars. E.g.
print(get_all_outputs(disciplines))
Out:
['y_31', 'y_32', 'g_3', 'y_4', 'y_23', 'y_21', 'y_24', 'y_2', 'y_11', 'y_12', 'g_2', 'y_3', 'y_14', 'g_1', 'y_34', 'y_1']
Get discipline schemas for inputs, outputs and options¶
The function
get_discipline_inputs_schema()returns the inputs of a discipline. E.g.
print(get_discipline_inputs_schema(disciplines[0]))
Out:
{'$schema': 'http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema', 'type': 'object', 'properties': {'y_23': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}, 'x_3': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}, 'x_shared': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}}, 'required': ['x_3', 'x_shared', 'y_23']}
The function
get_discipline_outputs_schema()returns the outputs of a discipline. E.g.
print(get_discipline_outputs_schema(disciplines[0]))
Out:
{'$schema': 'http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema', 'type': 'object', 'properties': {'y_32': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}, 'y_31': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}, 'g_3': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}, 'y_3': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}, 'y_34': {'type': 'array', 'items': {'type': 'number'}}}, 'required': ['g_3', 'y_3', 'y_31', 'y_32', 'y_34']}
The function
get_discipline_options_schema()returns the options of a discipline. E.g.
print(get_discipline_options_schema("SobieskiMission"))
Out:
{'$schema': 'http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema', 'type': 'object', 'properties': {'linearization_mode': {'description': 'Linearization mode', 'enum': ['auto', 'direct', 'reverse', 'adjoint'], 'type': 'string'}, 'jac_approx_type': {'description': 'Jacobian approximation type', 'enum': ['finite_differences', 'complex_step'], 'type': 'string'}, 'jax_approx_step': {'minimum': 0, 'exclusiveMinimum': True, 'description': 'Step for finite differences or complex step for Jacobian approximation', 'type': 'number'}, 'jac_approx_use_threading': {'description': 'if True, use Threads instead of processes\n to parallelize the execution. \nMultiprocessing will serialize all the disciplines, \nwhile multithreading will share all the memory.\n This is important to note if you want to execute the same\n discipline multiple times, you shall use multiprocessing', 'type': 'boolean'}, 'jac_approx_wait_time': {'description': 'Time waited between two forks of the process or thread when using parallel jacobian approximations (parallel=True)', 'minimum': 0, 'type': 'number'}, 'jac_approx_n_processes': {'minimum': 1, 'description': 'maximum number of processors or threads on \nwhich the jacobian approximation is performed\n by default, 1 means no parallel calculations', 'type': 'integer'}, 'cache_type': {'description': 'Type of cache to be used. \nBy default, simple cache stores the last execution inputs and outputs \nin memory only to avoid computation of the outputs if the inputs are identical.\n To store more executions, use HDF5 caches, which stores data on the disk.\n There is a hashing mechanism which avoids reading on the disk for every calculation.', 'type': 'string'}, 'cache_tolerance': {'minimum': 0, 'description': 'Numerical tolerance on the relative norm of input vectors \n to consider that two sets of inputs are equal, and that the outputs may therefore be returned from the cache without calculations.', 'type': 'number'}, 'cache_hdf_file': {'format': 'uri', 'description': 'Path to the HDF5 file to store the cache data.', 'type': 'string'}, 'cache_hdf_node_name': {'description': 'Name of the HDF dataset to store the discipline\n data. If None, the discipline name is used.', 'type': 'string'}, 'dtype': {'description': 'type of data, either "float64" or "complex128". :type dtype: str', 'type': 'string'}, 'enable_delay': {'type': 'boolean'}}, 'required': ['dtype', 'enable_delay']}
The function
get_discipline_options_defaults()can get the default option values of a discipline. E.g.
print(get_discipline_options_defaults("SobieskiMission"))
Out:
{'dtype': 'float64', 'enable_delay': False}
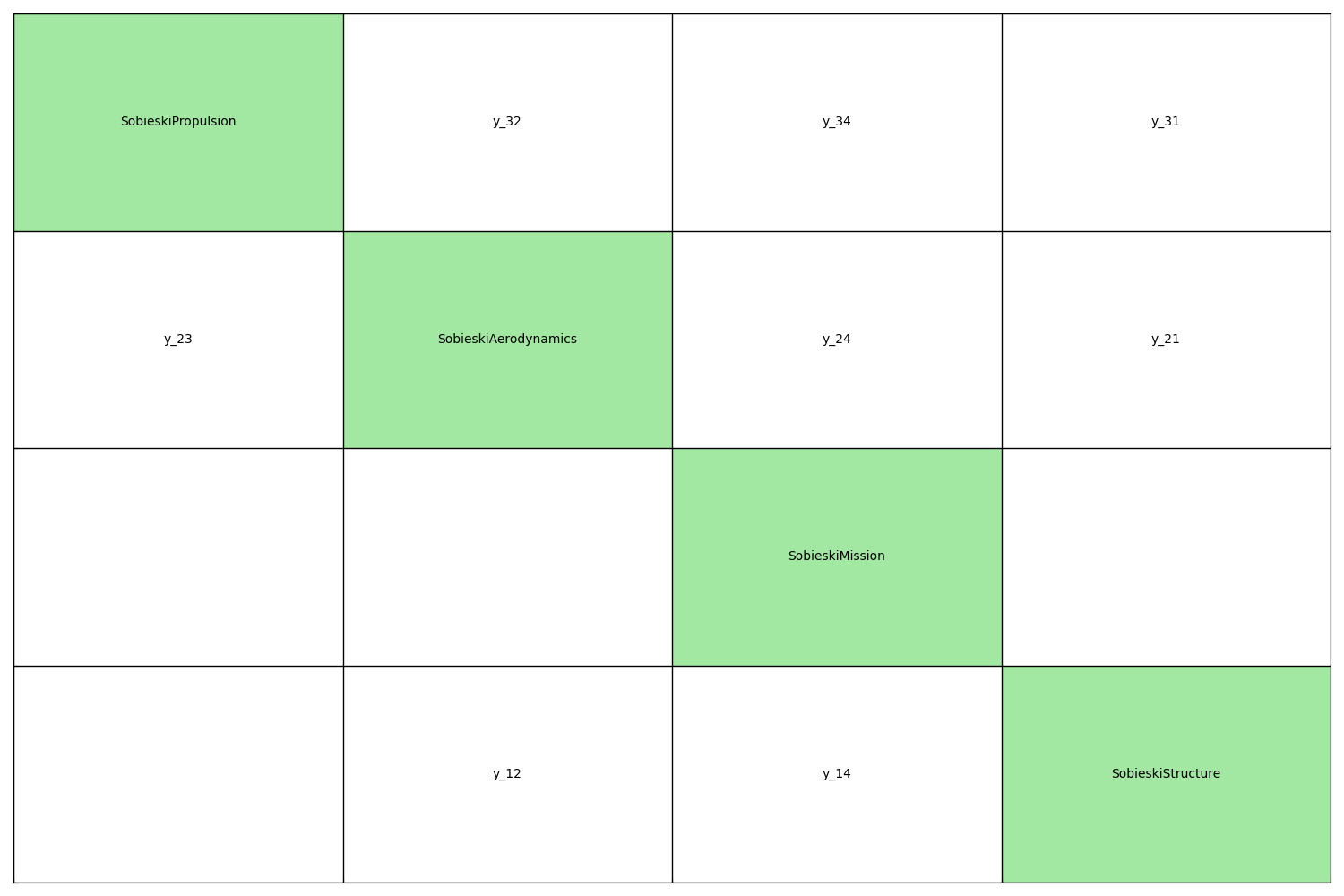
Plot coupling structure¶
The generate_coupling_graph() function plots the
coupling graph of a set of MDODiscipline:
generate_coupling_graph(disciplines, file_path="full_coupling_graph.pdf")
generate_coupling_graph(
disciplines, file_path="condensed_coupling_graph.pdf", full=False
)
The generate_n2_plot() function plots the N2 diagram of
a set of MDODiscipline:
generate_n2_plot(disciplines, save=False, show=True)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.488 seconds)
