Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Comparing sensitivity indices¶
from __future__ import annotations
from gemseo import configure_logger
from gemseo.problems.uncertainty.ishigami.ishigami_discipline import IshigamiDiscipline
from gemseo.problems.uncertainty.ishigami.ishigami_space import IshigamiSpace
from gemseo.uncertainty.sensitivity.correlation.analysis import CorrelationAnalysis
from gemseo.uncertainty.sensitivity.morris.analysis import MorrisAnalysis
configure_logger()
<RootLogger root (INFO)>
In this example, we consider the Ishigami function [IH90]
implemented as an MDODiscipline by the IshigamiDiscipline.
It is commonly used
with the independent random variables \(X_1\), \(X_2\) and \(X_3\)
uniformly distributed between \(-\pi\) and \(\pi\)
and defined in the IshigamiSpace.
discipline = IshigamiDiscipline()
uncertain_space = IshigamiSpace()
We would like to carry out two sensitivity analyses, e.g. a first one based on correlation coefficients and a second one based on the Morris methodology, and compare the results,
Firstly,
we create a CorrelationAnalysis and compute the sensitivity indices:
correlation = CorrelationAnalysis([discipline], uncertain_space, 10)
correlation.compute_indices()
WARNING - 08:55:20: No coupling in MDA, switching chain_linearize to True.
INFO - 08:55:20:
INFO - 08:55:20: *** Start CorrelationAnalysisSamplingPhase execution ***
INFO - 08:55:20: CorrelationAnalysisSamplingPhase
INFO - 08:55:20: Disciplines: IshigamiDiscipline
INFO - 08:55:20: MDO formulation: MDF
INFO - 08:55:20: Running the algorithm OT_MONTE_CARLO:
INFO - 08:55:20: 10%|█ | 1/10 [00:00<00:00, 146.03 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 20%|██ | 2/10 [00:00<00:00, 253.87 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 30%|███ | 3/10 [00:00<00:00, 339.66 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 40%|████ | 4/10 [00:00<00:00, 410.19 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 50%|█████ | 5/10 [00:00<00:00, 468.85 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 60%|██████ | 6/10 [00:00<00:00, 518.01 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 70%|███████ | 7/10 [00:00<00:00, 558.13 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 80%|████████ | 8/10 [00:00<00:00, 594.46 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 90%|█████████ | 9/10 [00:00<00:00, 620.99 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:00<00:00, 648.71 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: *** End CorrelationAnalysisSamplingPhase execution (time: 0:00:00.028532) ***
{<Method.KENDALL: 'Kendall'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.55555556]), 'x2': array([0.02222222]), 'x3': array([-0.11111111])}]}, <Method.PCC: 'PCC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.84696461]), 'x2': array([0.68814608]), 'x3': array([-0.29846394])}]}, <Method.PEARSON: 'Pearson'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.685388]), 'x2': array([0.09681897]), 'x3': array([-0.23027298])}]}, <Method.PRCC: 'PRCC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.90374102]), 'x2': array([0.76539572]), 'x3': array([-0.02232206])}]}, <Method.SPEARMAN: 'Spearman'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.74545455]), 'x2': array([0.04242424]), 'x3': array([-0.09090909])}]}, <Method.SRC: 'SRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.94001308]), 'x2': array([0.55748872]), 'x3': array([-0.16157012])}]}, <Method.SRRC: 'SRRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([1.06252802]), 'x2': array([0.60167726]), 'x3': array([-0.00959941])}]}, <Method.SSRC: 'SSRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.88362459]), 'x2': array([0.31079367]), 'x3': array([0.0261049])}]}}
Then,
we create an MorrisAnalysis and compute the sensitivity indices:
morris = MorrisAnalysis([discipline], uncertain_space, 10)
morris.compute_indices()
WARNING - 08:55:20: No coupling in MDA, switching chain_linearize to True.
WARNING - 08:55:20: No coupling in MDA, switching chain_linearize to True.
INFO - 08:55:20:
INFO - 08:55:20: *** Start MorrisAnalysisSamplingPhase execution ***
INFO - 08:55:20: MorrisAnalysisSamplingPhase
INFO - 08:55:20: Disciplines: _OATSensitivity
INFO - 08:55:20: MDO formulation: MDF
INFO - 08:55:20: Running the algorithm lhs:
INFO - 08:55:20: 50%|█████ | 1/2 [00:00<00:00, 63.17 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: 100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:00<00:00, 100.53 it/sec]
INFO - 08:55:20: *** End MorrisAnalysisSamplingPhase execution (time: 0:00:00.031052) ***
{'MU': {'y': [{'x1': array([0.73532408]), 'x2': array([-0.05115399]), 'x3': array([-1.6024484])}]}, 'MU_STAR': {'y': [{'x1': array([0.76770333]), 'x2': array([2.09435091]), 'x3': array([1.6024484])}]}, 'SIGMA': {'y': [{'x1': array([0.76770333]), 'x2': array([2.09435091]), 'x3': array([1.58984353])}]}, 'RELATIVE_SIGMA': {'y': [{'x1': array([1.]), 'x2': array([1.]), 'x3': array([0.99213399])}]}, 'MIN': {'y': [{'x1': array([0.03237925]), 'x2': array([2.04319692]), 'x3': array([0.01260487])}]}, 'MAX': {'y': [{'x1': array([1.50302741]), 'x2': array([2.14550491]), 'x3': array([3.19229192])}]}}
Lastly,
we compare these analyses
with the graphical method BaseSensitivityAnalysis.plot_comparison(),
either using a bar chart:
morris.plot_comparison(correlation, "y", use_bar_plot=True, save=False, show=True)
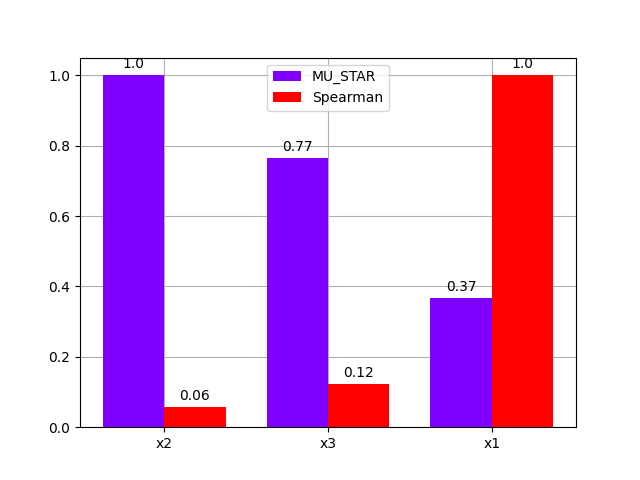
<gemseo.post.dataset.bars.BarPlot object at 0x7f1df75d31f0>
or a radar plot:
morris.plot_comparison(correlation, "y", use_bar_plot=False, save=False, show=True)
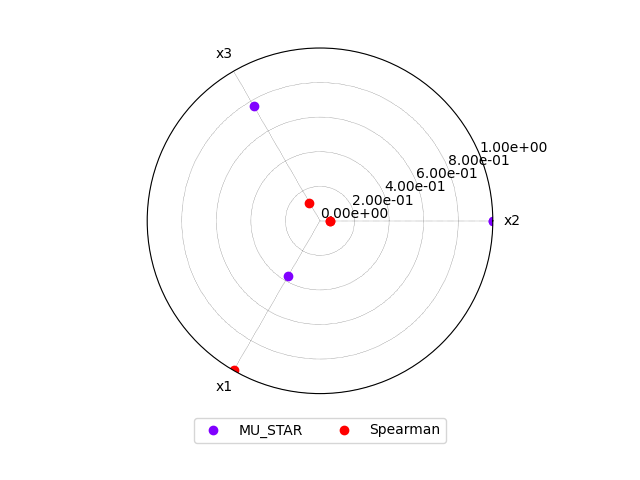
<gemseo.post.dataset.radar_chart.RadarChart object at 0x7f1dd3375430>
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.345 seconds)
