Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Correlation analysis¶
from __future__ import annotations
import pprint
from gemseo.uncertainty.sensitivity.correlation.analysis import CorrelationAnalysis
from gemseo.uncertainty.use_cases.ishigami.ishigami_discipline import IshigamiDiscipline
from gemseo.uncertainty.use_cases.ishigami.ishigami_space import IshigamiSpace
In this example, we consider the Ishigami function [IH90]
implemented as an MDODiscipline by the IshigamiDiscipline.
It is commonly used
with the independent random variables \(X_1\), \(X_2\) and \(X_3\)
uniformly distributed between \(-\pi\) and \(\pi\)
and defined in the IshigamiSpace.
discipline = IshigamiDiscipline()
uncertain_space = IshigamiSpace()
Then,
we run sensitivity analysis of type CorrelationAnalysis:
sensitivity_analysis = CorrelationAnalysis([discipline], uncertain_space, 1000)
sensitivity_analysis.compute_indices()
{<Method.KENDALL: 'Kendall'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.31460661]), 'x2': array([0.02366366]), 'x3': array([0.0297978])}]}, <Method.PCC: 'PCC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.46282123]), 'x2': array([0.0306214]), 'x3': array([0.0512473])}]}, <Method.PEARSON: 'Pearson'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.46230446]), 'x2': array([0.02059071]), 'x3': array([0.04979026])}]}, <Method.PRCC: 'PRCC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.47248718]), 'x2': array([0.04368652]), 'x3': array([0.0419606])}]}, <Method.SPEARMAN: 'Spearman'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.47177886]), 'x2': array([0.03220921]), 'x3': array([0.04128518])}]}, <Method.SRC: 'SRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.46220697]), 'x2': array([0.027121]), 'x3': array([0.04542585])}]}, <Method.SRRC: 'SRRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.4718925]), 'x2': array([0.03849088]), 'x3': array([0.03696642])}]}, <Method.SSRC: 'SSRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.21363529]), 'x2': array([0.00073555]), 'x3': array([0.00206351])}]}}
The resulting indices are
the Pearson correlation coefficients,
the Spearman correlation coefficients,
the Partial Correlation Coefficients (PCC),
the Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients (PRCC),
the Standard Regression Coefficients (SRC),
the Standard Rank Regression Coefficient (SRRC),
the Signed Standard Rank Regression Coefficient (SSRRC):
pprint.pprint(sensitivity_analysis.indices)
{<Method.KENDALL: 'Kendall'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.31460661]),
'x2': array([0.02366366]),
'x3': array([0.0297978])}]},
<Method.PCC: 'PCC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.46282123]),
'x2': array([0.0306214]),
'x3': array([0.0512473])}]},
<Method.PRCC: 'PRCC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.47248718]),
'x2': array([0.04368652]),
'x3': array([0.0419606])}]},
<Method.PEARSON: 'Pearson'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.46230446]),
'x2': array([0.02059071]),
'x3': array([0.04979026])}]},
<Method.SRC: 'SRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.46220697]),
'x2': array([0.027121]),
'x3': array([0.04542585])}]},
<Method.SRRC: 'SRRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.4718925]),
'x2': array([0.03849088]),
'x3': array([0.03696642])}]},
<Method.SSRC: 'SSRC'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.21363529]),
'x2': array([0.00073555]),
'x3': array([0.00206351])}]},
<Method.SPEARMAN: 'Spearman'>: {'y': [{'x1': array([0.47177886]),
'x2': array([0.03220921]),
'x3': array([0.04128518])}]}}
The main indices corresponds to the Spearman correlation indices
(this main method can be changed with CorrelationAnalysis.main_method):
pprint.pprint(sensitivity_analysis.main_indices)
{'y': [{'x1': array([0.47177886]),
'x2': array([0.03220921]),
'x3': array([0.04128518])}]}
We can also sort the input parameters by decreasing order of influence:
print(sensitivity_analysis.sort_parameters("y"))
['x1', 'x3', 'x2']
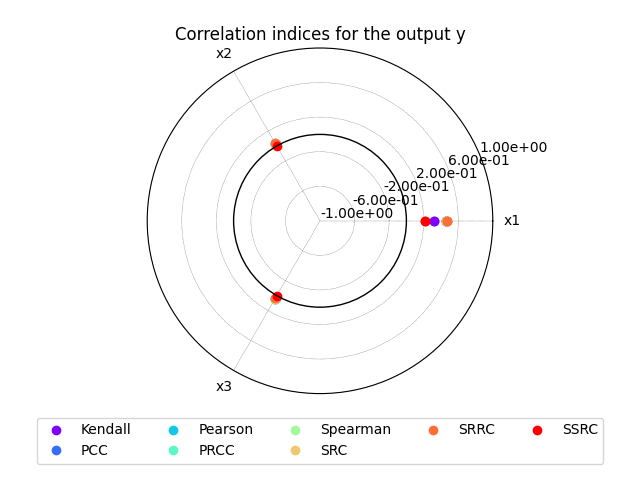
Lastly,
we can use the method CorrelationAnalysis.plot()
to visualize the different correlation coefficients:
sensitivity_analysis.plot("y", save=False, show=True)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.882 seconds)
