Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Self-Organizing Map¶
In this example, we illustrate the use of the SOM plot
on the Sobieski’s SSBJ problem.
from __future__ import annotations
from gemseo import configure_logger
from gemseo import create_discipline
from gemseo import create_scenario
from gemseo.problems.sobieski.core.problem import SobieskiProblem
Import¶
The first step is to import some high-level functions and a method to get the design space.
configure_logger()
<RootLogger root (INFO)>
Description¶
The SOM post-processing performs a Self Organizing Map
clustering on the optimization history.
A SOM is a 2D representation of a design of experiments
which requires dimensionality reduction since it may be in a very high dimension.
A SOM is built by using an unsupervised artificial neural network
[KSH01].
A map of size n_x.n_y is generated, where
n_x is the number of neurons in the \(x\) direction and n_y
is the number of neurons in the \(y\) direction. The design space
(whatever the dimension) is reduced to a 2D representation based on
n_x.n_y neurons. Samples are clustered to a neuron when their design
variables are close in terms of their L2 norm. A neuron is always located at the
same place on a map. Each neuron is colored according to the average value for
a given criterion. This helps to qualitatively analyze whether parts of the design
space are good according to some criteria and not for others, and where
compromises should be made. A white neuron has no sample associated with
it: not enough evaluations were provided to train the SOM.
SOM’s provide a qualitative view of the objective function, the constraints, and of their relative behaviors.
Create disciplines¶
At this point, we instantiate the disciplines of Sobieski’s SSBJ problem: Propulsion, Aerodynamics, Structure and Mission
disciplines = create_discipline(
[
"SobieskiPropulsion",
"SobieskiAerodynamics",
"SobieskiStructure",
"SobieskiMission",
]
)
Create design space¶
We also read the design space from the SobieskiProblem.
design_space = SobieskiProblem().design_space
Create and execute scenario¶
The next step is to build an MDO scenario in order to maximize the range, encoded ‘y_4’, with respect to the design parameters, while satisfying the inequality constraints ‘g_1’, ‘g_2’ and ‘g_3’. We can use the MDF formulation, the Monte Carlo DOE algorithm and 30 samples.
scenario = create_scenario(
disciplines,
formulation="MDF",
objective_name="y_4",
maximize_objective=True,
design_space=design_space,
scenario_type="DOE",
)
scenario.set_differentiation_method()
for constraint in ["g_1", "g_2", "g_3"]:
scenario.add_constraint(constraint, "ineq")
scenario.execute({"algo": "OT_MONTE_CARLO", "n_samples": 30})
INFO - 08:41:23:
INFO - 08:41:23: *** Start DOEScenario execution ***
INFO - 08:41:23: DOEScenario
INFO - 08:41:23: Disciplines: SobieskiAerodynamics SobieskiMission SobieskiPropulsion SobieskiStructure
INFO - 08:41:23: MDO formulation: MDF
INFO - 08:41:23: Optimization problem:
INFO - 08:41:23: minimize -y_4(x_shared, x_1, x_2, x_3)
INFO - 08:41:23: with respect to x_1, x_2, x_3, x_shared
INFO - 08:41:23: subject to constraints:
INFO - 08:41:23: g_1(x_shared, x_1, x_2, x_3) <= 0.0
INFO - 08:41:23: g_2(x_shared, x_1, x_2, x_3) <= 0.0
INFO - 08:41:23: g_3(x_shared, x_1, x_2, x_3) <= 0.0
INFO - 08:41:23: over the design space:
INFO - 08:41:23: +-------------+-------------+-------+-------------+-------+
INFO - 08:41:23: | name | lower_bound | value | upper_bound | type |
INFO - 08:41:23: +-------------+-------------+-------+-------------+-------+
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_shared[0] | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.09 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_shared[1] | 30000 | 45000 | 60000 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_shared[2] | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_shared[3] | 2.5 | 5.5 | 8.5 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_shared[4] | 40 | 55 | 70 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_shared[5] | 500 | 1000 | 1500 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_1[0] | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.4 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_1[1] | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_2 | 0.75 | 1 | 1.25 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: | x_3 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | float |
INFO - 08:41:23: +-------------+-------------+-------+-------------+-------+
INFO - 08:41:23: Solving optimization problem with algorithm OT_MONTE_CARLO:
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 0%| | 0/30 [00:00<?, ?it]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 3%|▎ | 1/30 [00:00<00:02, 9.80 it/sec, obj=-166]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 7%|▋ | 2/30 [00:00<00:01, 14.33 it/sec, obj=-484]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 10%|█ | 3/30 [00:00<00:01, 16.93 it/sec, obj=-481]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 13%|█▎ | 4/30 [00:00<00:01, 18.65 it/sec, obj=-384]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 17%|█▋ | 5/30 [00:00<00:01, 19.92 it/sec, obj=-1.14e+3]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 20%|██ | 6/30 [00:00<00:01, 20.87 it/sec, obj=-290]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 23%|██▎ | 7/30 [00:00<00:01, 21.33 it/sec, obj=-630]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 27%|██▋ | 8/30 [00:00<00:01, 21.46 it/sec, obj=-346]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 30%|███ | 9/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.76 it/sec, obj=-626]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 33%|███▎ | 10/30 [00:00<00:00, 22.02 it/sec, obj=-621]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 37%|███▋ | 11/30 [00:00<00:00, 22.22 it/sec, obj=-280]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 40%|████ | 12/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.88 it/sec, obj=-288]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 43%|████▎ | 13/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.61 it/sec, obj=-257]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 47%|████▋ | 14/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.36 it/sec, obj=-367]
INFO - 08:41:23: ... 50%|█████ | 15/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.30 it/sec, obj=-1.08e+3]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 53%|█████▎ | 16/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.46 it/sec, obj=-344]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 57%|█████▋ | 17/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.38 it/sec, obj=-368]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 60%|██████ | 18/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.32 it/sec, obj=-253]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 63%|██████▎ | 19/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.19 it/sec, obj=-129]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 67%|██████▋ | 20/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.17 it/sec, obj=-1.07e+3]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 70%|███████ | 21/30 [00:00<00:00, 21.39 it/sec, obj=-341]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 73%|███████▎ | 22/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.52 it/sec, obj=-1e+3]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 77%|███████▋ | 23/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.22 it/sec, obj=-586]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 80%|████████ | 24/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.35 it/sec, obj=-483]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 83%|████████▎ | 25/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.53 it/sec, obj=-392]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 87%|████████▋ | 26/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.71 it/sec, obj=-406]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 90%|█████████ | 27/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.60 it/sec, obj=-207]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 93%|█████████▎| 28/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.76 it/sec, obj=-702]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 97%|█████████▋| 29/30 [00:01<00:00, 21.99 it/sec, obj=-423]
INFO - 08:41:24: ... 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:01<00:00, 22.07 it/sec, obj=-664]
INFO - 08:41:24: Optimization result:
INFO - 08:41:24: Optimizer info:
INFO - 08:41:24: Status: None
INFO - 08:41:24: Message: None
INFO - 08:41:24: Number of calls to the objective function by the optimizer: 30
INFO - 08:41:24: Solution:
INFO - 08:41:24: The solution is feasible.
INFO - 08:41:24: Objective: -367.45728393799953
INFO - 08:41:24: Standardized constraints:
INFO - 08:41:24: g_1 = [-0.02478574 -0.00310924 -0.00855146 -0.01702654 -0.02484732 -0.04764585
INFO - 08:41:24: -0.19235415]
INFO - 08:41:24: g_2 = -0.09000000000000008
INFO - 08:41:24: g_3 = [-0.98722984 -0.01277016 -0.60760341 -0.0557087 ]
INFO - 08:41:24: Design space:
INFO - 08:41:24: +-------------+-------------+---------------------+-------------+-------+
INFO - 08:41:24: | name | lower_bound | value | upper_bound | type |
INFO - 08:41:24: +-------------+-------------+---------------------+-------------+-------+
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_shared[0] | 0.01 | 0.01230934749207792 | 0.09 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_shared[1] | 30000 | 43456.87364611478 | 60000 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_shared[2] | 1.4 | 1.731884935123487 | 1.8 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_shared[3] | 2.5 | 3.894765253193514 | 8.5 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_shared[4] | 40 | 57.92631048228255 | 70 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_shared[5] | 500 | 520.4048463450415 | 1500 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_1[0] | 0.1 | 0.3994784918586811 | 0.4 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_1[1] | 0.75 | 0.9500312867674923 | 1.25 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_2 | 0.75 | 1.205851870260564 | 1.25 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: | x_3 | 0.1 | 0.2108042391973412 | 1 | float |
INFO - 08:41:24: +-------------+-------------+---------------------+-------------+-------+
INFO - 08:41:24: *** End DOEScenario execution (time: 0:00:01.377639) ***
{'eval_jac': False, 'n_samples': 30, 'algo': 'OT_MONTE_CARLO'}
Post-process scenario¶
Lastly, we post-process the scenario by means of the
SOM plot which performs a self organizing map
clustering on optimization history.
Tip
Each post-processing method requires different inputs and offers a variety
of customization options. Use the high-level function
get_post_processing_options_schema() to print a table with
the options for any post-processing algorithm.
Or refer to our dedicated page:
Post-processing algorithms.
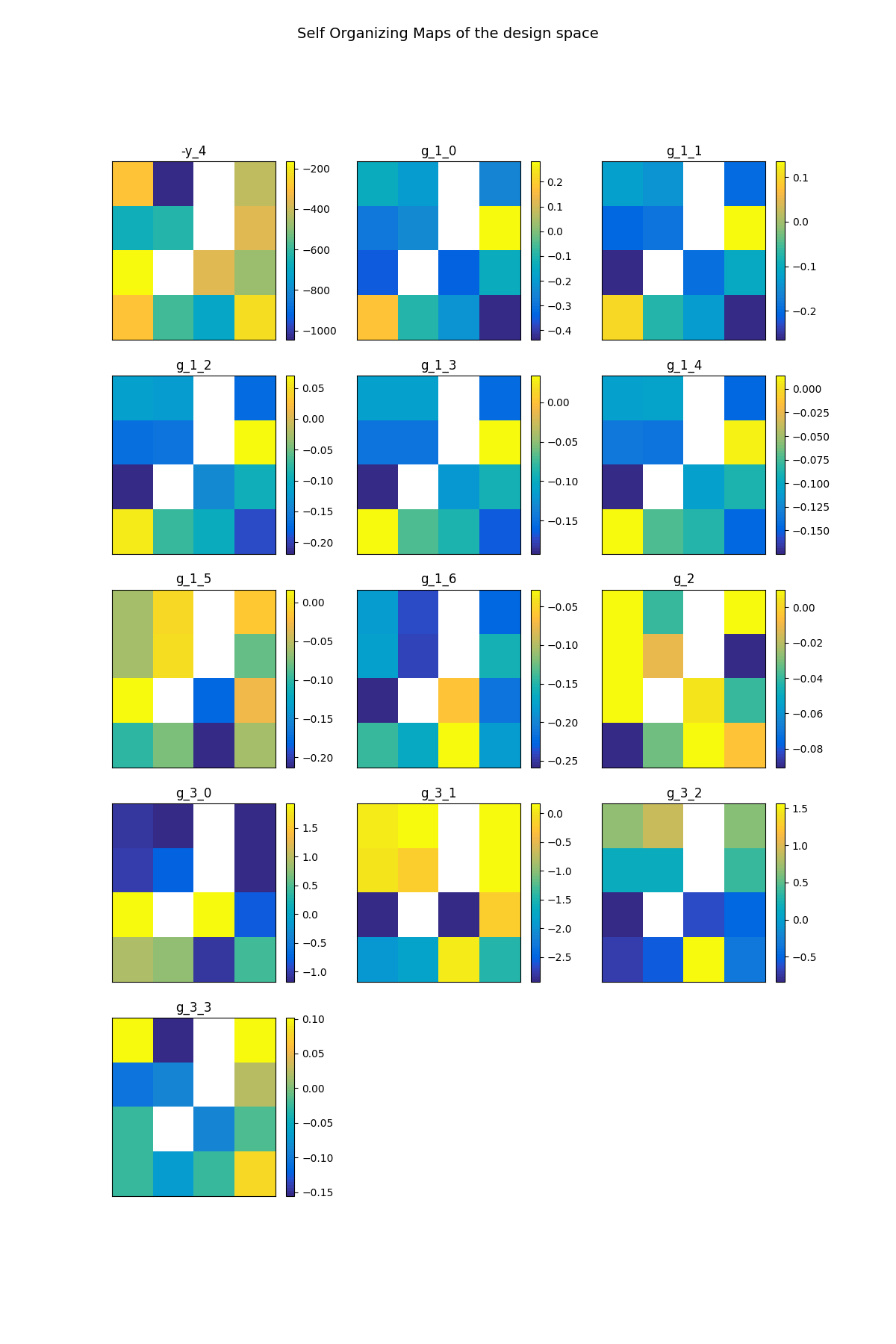
scenario.post_process("SOM", save=False, show=True)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/gemseo/envs/5.0.1/lib/python3.9/site-packages/genson/schema/strategies/base.py:42: UserWarning: Schema incompatible. Keyword 'description' has conflicting values ('The width and height of the figure in inches, e.g. ``(w, h)``.\nIf ``None``, use the :attr:`.OptPostProcessor.DEFAULT_FIG_SIZE`\nof the post-processor.' vs. 'The width and height of the figure in inches, e.g. `(w, h)`.\nIf ``None``, use the :attr:`.OptPostProcessor.DEFAULT_FIG_SIZE`\nof the post-processor.'). Using 'The width and height of the figure in inches, e.g. ``(w, h)``.\nIf ``None``, use the :attr:`.OptPostProcessor.DEFAULT_FIG_SIZE`\nof the post-processor.'
warn(('Schema incompatible. Keyword {0!r} has conflicting '
INFO - 08:41:24: Building Self Organizing Map from optimization history:
INFO - 08:41:24: Number of neurons in x direction = 4
INFO - 08:41:24: Number of neurons in y direction = 4
<gemseo.post.som.SOM object at 0x7f8729a0e220>
Figure SOM example on the Sobieski problem. illustrates another SOM on the Sobieski
use case. The optimization method is a (costly) derivative free algorithm
(NLOPT_COBYLA), indeed all the relevant information for the optimization
is obtained at the cost of numerous evaluations of the functions. For
more details, please read the paper by
[KJO+06] on wing MDO post-processing
using SOM.
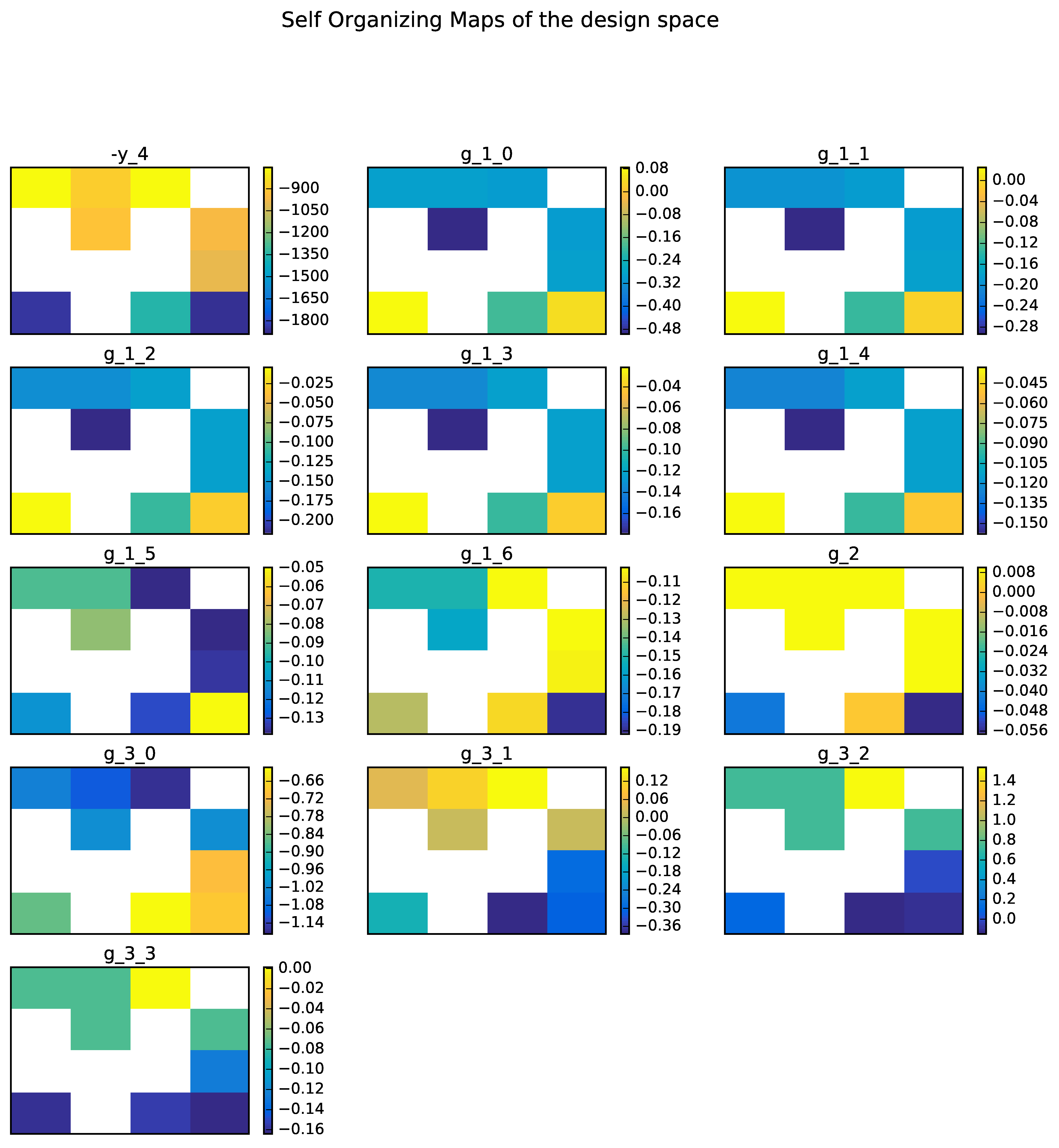
SOM example on the Sobieski problem.¶
A DOE may also be a good way to produce SOM maps. Figure SOM example on the Sobieski problem with a 10 000 samples DOE. shows an example with 10000 points on the same test case. This produces more relevant SOM plots.
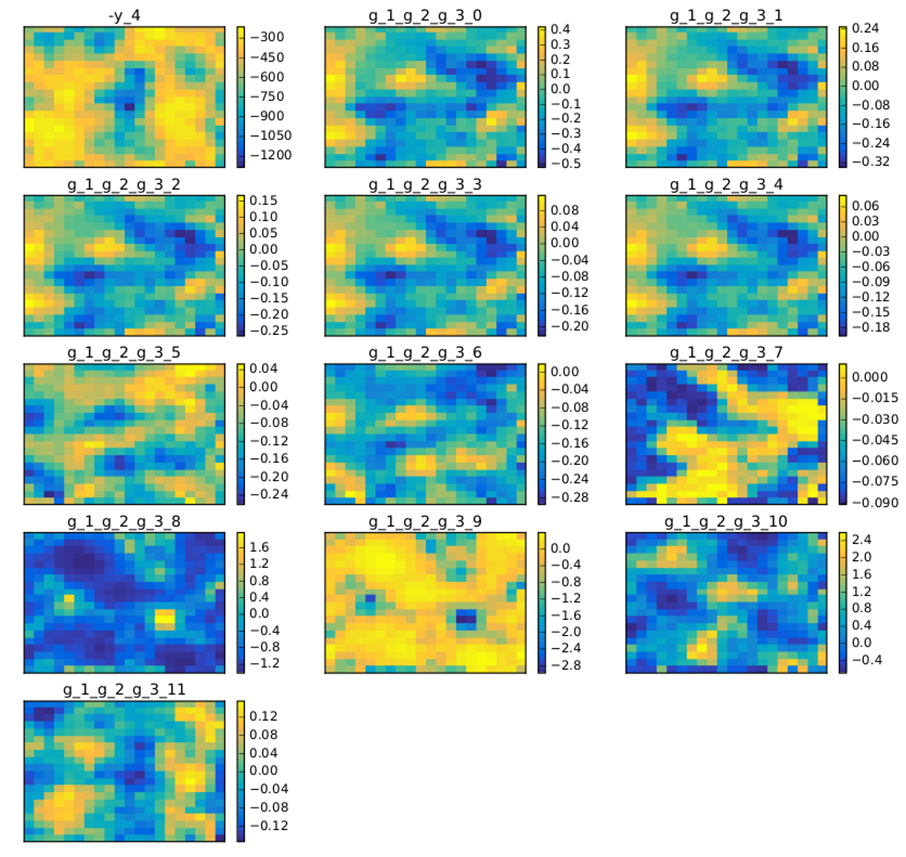
SOM example on the Sobieski problem with a 10 000 samples DOE.¶
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.447 seconds)
