Caching and recording discipline data¶
GEMSEO offers various features that allow to record and cache the values of discipline inputs and outputs, as well as its jacobian.
Introduction¶
Executing a discipline triggers a simulation which can be costly.
The first need for caching is to avoid duplicate simulations with the same inputs.
Then, the generated data contain valuable information which one may want to analyze after or during the execution, so storing this data on the disk is useful.
Finally, in case of machine crash, restarting the MDO process from scratch may be a waste of computational resources. Again, storing the input and output data on the disk avoids duplicate execution in case of crash.
In GEMSEO, each MDODiscipline has a cache.
>>> from gemseo.api import create_discipline
>>> discipline = create_discipline('AnalyticDiscipline', name='my_discipline', expressions_dict={'y':'2*x'})
>>> print(discipline.cache)
my_discipline
| Type: SimpleCache
| Input names: None
| Output names: None
| Length: 0
| Tolerance: 0.0
Setting a cache policy¶
All disciplines have the MDODiscipline.SIMPLE_CACHE cache policy enabled by default.
Other ones are MDODiscipline.MEMORY_FULL_CACHE and
MDODiscipline.HDF5_CACHE.
The cache policy can be defined by means of the MDODiscipline.set_cache_policy() method:
- MDODiscipline.set_cache_policy(cache_type='SimpleCache', cache_tolerance=0.0, cache_hdf_file=None, cache_hdf_node_name=None, is_memory_shared=True)[source]
Set the type of cache to use and the tolerance level.
This method defines when the output data have to be cached according to the distance between the corresponding input data and the input data already cached for which output data are also cached.
The cache can be either a
SimpleCacherecording the last execution or a cache storing all executions, e.g.MemoryFullCacheandHDF5Cache. Caching data can be either in-memory, e.g.SimpleCacheandMemoryFullCache, or on the disk, e.g.HDF5Cache.The attribute
CacheFactory.cachesprovides the available caches types.- Parameters
cache_type (str) –
The type of cache.
By default it is set to SimpleCache.
cache_tolerance (float) –
The maximum relative norm of the difference between two input arrays to consider that two input arrays are equal.
By default it is set to 0.0.
cache_hdf_file (Optional[Union[str, pathlib.Path]]) –
The path to the HDF file to store the data; this argument is mandatory when the
HDF5Cachepolicy is used.By default it is set to None.
cache_hdf_node_name (Optional[str]) –
The name of the HDF file node to store the discipline data. If None,
nameis used.By default it is set to None.
is_memory_shared (bool) –
Whether to store the data with a shared memory dictionary, which makes the cache compatible with multiprocessing.
By default it is set to True.
- Return type
None
>>> from gemseo.api import create_discipline
>>> discipline = create_discipline('AnalyticDiscipline', name='my_discipline', expressions_dict={'y':'2*x'})
>>> print(discipline.cache)
my_discipline
| Type: SimpleCache
| Input names: None
| Output names: None
| Length: 0
| Tolerance: 0.0
>>> discipline.set_cache_policy(discipline.MEMORY_FULL_CACHE)
>>> print(discipline.cache)
my_discipline
| Type: MemoryFullCache
| Input names: None
| Output names: None
| Length: 0
| Tolerance: 0.0
The different cache policies¶
Simple cache: storing the last execution¶
The simplest cache strategy in GEMSEO only stores the last execution data (inputs, outputs, and eventually the Jacobian matrix) in memory.
This cache strategy is implemented by means of the SimpleCache class:
- class gemseo.caches.simple_cache.SimpleCache(tolerance=0.0, name=None)[source]
Simple discipline cache based on a dictionary.
Only caches the last execution.
Initialize cache tolerance. By default, don’t use approximate cache. It is up to the user to choose to optimize CPU time with this or not.
could be something like 2 * finfo(float).eps
- Parameters
tolerance (float) –
Tolerance that defines if two input vectors are equal and cached data shall be returned. If 0, no approximation is made. Default: 0.
By default it is set to 0.0.
name (str) –
Name of the cache.
By default it is set to None.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> cache = SimpleCache()
Methods:
cache_jacobian(input_data, input_names, jacobian)Cache jacobian data to avoid re evaluation.
cache_outputs(input_data, input_names, ...)Cache data to avoid re evaluation.
clear()Clear the cache.
get_all_data([as_iterator])Read all the data in the cache.
get_data(index, **options)Returns an elementary sample.
Retrieve the last execution inputs.
Retrieve the last execution outputs.
Get the length of the cache, ie the number of stored elements.
get_outputs(input_data[, input_names])Check if the discipline has already been evaluated for the given input data dictionary.
Attributes:
Return the inputs names.
Get the maximal length of the cache (the maximal number of stored elements).
Return the outputs names.
List of samples indices.
Return the variables sizes.
- cache_jacobian(input_data, input_names, jacobian)[source]
Cache jacobian data to avoid re evaluation.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data to cache.
input_names (list(str)) – List of input data names.
jacobian (dict) – Jacobian to cache.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> jacobian = {'y': {'x': array([3.])}} >>> cache.cache_jacobian(data, ['x'], jacobian) (None, {'y': {'x': array([3.])}})
- cache_outputs(input_data, input_names, output_data, output_names=None)[source]
Cache data to avoid re evaluation.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data to cache.
input_names (list(str)) – List of input data names.
output_data (dict) – Output data to cache.
output_names (list(str)) –
List of output data names. If None, use all output names. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache[1] {'y': array([2.]), 'x': array([1.])}
- clear()[source]
Clear the cache.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([.2])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_length() 1 >>> cache.clear() >>> cache.get_length() 0
- get_all_data(as_iterator=False)[source]
Read all the data in the cache.
- Parameters
as_iterator (bool) –
If True, return an iterator. Otherwise a dictionary. Default: False.
By default it is set to False.
- Returns
all_data – A dictionary of dictionaries for inputs, outputs and jacobian where keys are data indices.
- Return type
dict
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_all_data() {1: {'inputs': {'x': array([1.])}, 'jacobian': None, 'outputs': {'y': array([0.2])}}}
- get_data(index, **options)[source]
Returns an elementary sample.
- Parameters
index (int) – sample index.
options – getter options
- get_last_cached_inputs()[source]
Retrieve the last execution inputs.
- Returns
inputs – Last cached inputs.
- Return type
dict
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_last_cached_inputs() {'X': array([1.])}
- get_last_cached_outputs()[source]
Retrieve the last execution outputs.
- Returns
outputs – Last cached outputs.
- Return type
dict
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_last_cached_outputs() {'y': array([2.])}
- get_length()[source]
Get the length of the cache, ie the number of stored elements.
- Returns
length – Length of the cache.
- Return type
int
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_length() 1
- get_outputs(input_data, input_names=None)[source]
Check if the discipline has already been evaluated for the given input data dictionary. If True, return the associated cache, otherwise return None.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data dictionary to test for caching.
input_names (list(str)) –
List of input data names. If None, uses them all
By default it is set to None.
- Returns
output_data (dict) – Output data if there is no need to evaluate the discipline. None otherwise.
jacobian (dict) – Jacobian if there is no need to evaluate the discipline. None otherwise.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.simple_cache import SimpleCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = SimpleCache() >>> data = {'x': array([1.]), 'y': array([2.])} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_outputs({'x': array([1.])}, ['x']) ({'y': array([2.])}, None) >>> cache.get_outputs({'x': array([2.])}, ['x']) (None, None)
- property inputs_names
Return the inputs names.
- property max_length
Get the maximal length of the cache (the maximal number of stored elements).
- Returns
length – Maximal length of the cache.
- Return type
int
- property outputs_names
Return the outputs names.
- property samples_indices
List of samples indices.
- property varsizes
Return the variables sizes.
Memory cache: recording all executions in memory¶
The MemoryFullCache is the in-memory version of the HDF5Cache.
It allows to store several executions of a discipline in terms of both inputs, outputs and jacobian values into a dictionary.
This cache strategy is implemented by means of the MemoryFullCache class:
- class gemseo.caches.memory_full_cache.MemoryFullCache(tolerance=0.0, name=None, is_memory_shared=True)[source]
Cache using memory to cache all data.
Initialize a dictionary to cache data.
Initialize cache tolerance. By default, don’t use approximate cache. It is up to the user to choose to optimize CPU time with this or not could be something like 2 * finfo(float).eps
- Parameters
tolerance (float) –
Tolerance that defines if two input vectors are equal and cached data shall be returned. If 0, no approximation is made. Default: 0.
By default it is set to 0.0.
name (str) –
Name of the cache.
By default it is set to None.
is_memory_shared (bool) –
If True, a shared memory dict is used to store the data, which makes the cache compatible with multiprocessing. WARNING: if set to False, and multiple disciplines point to the same cache or the process is multiprocessed, there may be duplicate computations because the cache will not be shared among the processes.
By default it is set to True.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.memory_full_cache import MemoryFullCache >>> cache = MemoryFullCache()
Methods:
cache_jacobian(input_data, input_names, jacobian)Cache jacobian data to avoid re evaluation.
cache_outputs(input_data, input_names, ...)Cache data to avoid re evaluation.
clear()Clear the cache.
export_to_dataset([name, by_group, ...])Set Dataset from a cache.
export_to_ggobi(file_path[, inputs_names, ...])Export history to xml file format for ggobi tool.
get_all_data([as_iterator])Return all the data in the cache.
get_data(index, **options)Gets the data associated to a sample ID.
Retrieve the last execution inputs.
Retrieve the last execution outputs.
Get the length of the cache, ie the number of stored elements.
get_outputs(input_data[, input_names])Check if the discipline has already been evaluated for the given input data dictionary.
merge(other_cache)Merges an other cache with self.
Attributes:
Copy cache.
Return the inputs names.
Get the maximal length of the cache (the maximal number of stored elements).
Return the outputs names.
List of samples indices.
Return the variables sizes.
- cache_jacobian(input_data, input_names, jacobian)
Cache jacobian data to avoid re evaluation.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data to cache.
input_names (list(str)) – List of input data names.
jacobian (dict) – Jacobian to cache.
- cache_outputs(input_data, input_names, output_data, output_names=None)
Cache data to avoid re evaluation.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data to cache.
input_names (list(str)) – List of input data names.
output_data (dict) – Output data to cache.
output_names (list(str)) –
List of output data names. If None, use all output names. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
- clear()[source]
Clear the cache.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.memory_full_cache import MemoryFullCache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = MemoryFullCache() >>> for index in range(5): >>> data = {'x': array([1.])*index, 'y': array([.2])*index} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_length() 5 >>> cache.clear() >>> cache.get_length() 0
- property copy
Copy cache.
- export_to_dataset(name=None, by_group=True, categorize=True, inputs_names=None, outputs_names=None)
Set Dataset from a cache.
- Parameters
name (str) –
dataset name.
By default it is set to None.
by_group (bool) –
if True, store the data by group. Otherwise, store them by variables. Default: True
By default it is set to True.
categorize (bool) –
distinguish between the different groups of variables. Default: True.
By default it is set to True.
inputs_names (list(str)) –
list of inputs names. If None, use all inputs. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
outputs_names (list(str)) –
list of outputs names. If None, use all outputs. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
- export_to_ggobi(file_path, inputs_names=None, outputs_names=None)
Export history to xml file format for ggobi tool.
- Parameters
file_path (str) – Path to export the file.
inputs_names (list(str)) –
List of inputs to include in the export. By default, take all of them.
By default it is set to None.
outputs_names (list(str)) –
Names of outputs to export. By default, take all of them.
By default it is set to None.
- get_all_data(as_iterator=False)
Return all the data in the cache.
- Parameters
as_iterator (bool) –
If True, return an iterator. Otherwise a dictionary. Default: False.
By default it is set to False.
- Returns
all_data – A dictionary of dictionaries for inputs, outputs and jacobian where keys are data indices.
- Return type
dict
- get_data(index, **options)
Gets the data associated to a sample ID.
- Parameters
index (str) – sample ID.
options – options passed to the _read_data() method.
- Returns
input data, output data and jacobian.
- Return type
dict
- get_last_cached_inputs()
Retrieve the last execution inputs.
- Returns
inputs – Last cached inputs.
- Return type
dict
- get_last_cached_outputs()
Retrieve the last execution outputs.
- Returns
outputs – Last cached outputs.
- Return type
dict
- get_length()
Get the length of the cache, ie the number of stored elements.
- Returns
length – Length of the cache.
- Return type
int
- get_outputs(input_data, input_names=None)
Check if the discipline has already been evaluated for the given input data dictionary. If True, return the associated cache, otherwise return None.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data dictionary to test for caching.
input_names (list(str)) –
List of input data names.
By default it is set to None.
- Returns
output_data (dict) – Output data if there is no need to evaluate the discipline. None otherwise.
jacobian (dict) – Jacobian if there is no need to evaluate the discipline. None otherwise.
- property inputs_names
Return the inputs names.
- property max_length
Get the maximal length of the cache (the maximal number of stored elements).
- Returns
length – Maximal length of the cache.
- Return type
int
- merge(other_cache)
Merges an other cache with self.
- Parameters
other_cache (AbstractFullCache) – Cache to merge with the current one.
- property outputs_names
Return the outputs names.
- property samples_indices
List of samples indices.
- property varsizes
Return the variables sizes.
HDF5 cache: recording all executions on the disk¶
When all the execution data of the discipline shall be stored on the disk, the HDF5 cache policy can be used. HDF5 is a standard file format for storing simulation data. The following description is proposed by the HDF5 website:
“HDF5 is a data model, library, and file format for storing and managing data. It supports an unlimited variety of datatypes, and is designed for flexible and efficient I/O and for high volume and complex data. HDF5 is portable and is extensible, allowing applications to evolve in their use of HDF5. The HDF5 Technology suite includes tools and applications for managing, manipulating, viewing, and analyzing data in the HDF5 format.”
HDF5 manipulation libraries exist at least in C++, C, Java, Fortran and Python languages.
The HDFView application can be used to explore the data of the cache.
To manipulate the data, one may use the HDF5Cache class, which can import the file and read all the data,
or the data of a specific execution.
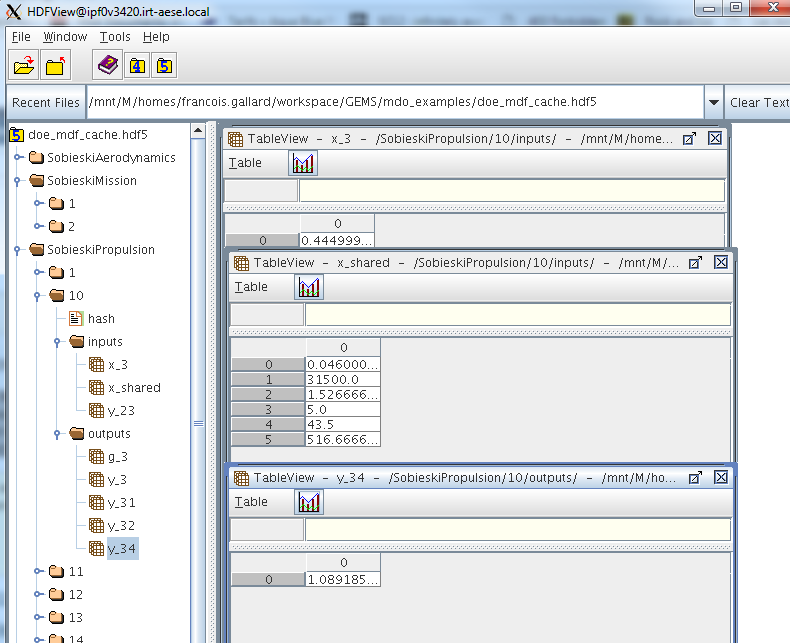
HDFView of the cache generated by a MDF DOE scenario execution on the SSBJ test case¶
This cache strategy is implemented by means of the HDF5Cache class:
- class gemseo.caches.hdf5_cache.HDF5Cache(hdf_file_path, hdf_node_path, tolerance=0.0, name=None)[source]
Cache using disk HDF5 file to store the data.
Initialize a singleton to access a HDF file. This singleton is used for multithreaded/multiprocessing access with a Lock.
Initialize cache tolerance. By default, don’t use approximate cache. It is up to the user to choose to optimize CPU time with this or not could be something like 2 * finfo(float).eps
- Parameters
hdf_file_path (str) – Path of the HDF file.
hdf_node_path (str) – Node of the HDF file.
tolerance (float) –
Tolerance that defines if two input vectors are equal and cached data shall be returned. If 0, no approximation is made. Default: 0.
By default it is set to 0.0.
name (str) –
Name of the cache.
By default it is set to None.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.hdf5_cache import HDF5Cache >>> cache = HDF5Cache('my_cache.h5', 'my_node')
Methods:
cache_jacobian(input_data, input_names, jacobian)Cache jacobian data to avoid re evaluation.
cache_outputs(input_data, input_names, ...)Cache data to avoid re evaluation.
clear()Clear the cache.
export_to_dataset([name, by_group, ...])Set Dataset from a cache.
export_to_ggobi(file_path[, inputs_names, ...])Export history to xml file format for ggobi tool.
get_all_data([as_iterator])Return all the data in the cache.
get_data(index, **options)Gets the data associated to a sample ID.
Retrieve the last execution inputs.
Retrieve the last execution outputs.
Get the length of the cache, ie the number of stored elements.
get_outputs(input_data[, input_names])Check if the discipline has already been evaluated for the given input data dictionary.
merge(other_cache)Merges an other cache with self.
update_file_format(hdf_file_path)Update the format of a HDF5 file.
Attributes:
Return the inputs names.
Get the maximal length of the cache (the maximal number of stored elements).
Return the outputs names.
List of samples indices.
Return the variables sizes.
- cache_jacobian(input_data, input_names, jacobian)
Cache jacobian data to avoid re evaluation.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data to cache.
input_names (list(str)) – List of input data names.
jacobian (dict) – Jacobian to cache.
- cache_outputs(input_data, input_names, output_data, output_names=None)
Cache data to avoid re evaluation.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data to cache.
input_names (list(str)) – List of input data names.
output_data (dict) – Output data to cache.
output_names (list(str)) –
List of output data names. If None, use all output names. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
- clear()[source]
Clear the cache.
Examples
>>> from gemseo.caches.hdf5_cache import HDF5Cache >>> from numpy import array >>> cache = HDF5Cache('my_cache.h5', 'my_node') >>> for index in range(5): >>> data = {'x': array([1.])*index, 'y': array([.2])*index} >>> cache.cache_outputs(data, ['x'], data, ['y']) >>> cache.get_length() 5 >>> cache.clear() >>> cache.get_length() 0
- export_to_dataset(name=None, by_group=True, categorize=True, inputs_names=None, outputs_names=None)
Set Dataset from a cache.
- Parameters
name (str) –
dataset name.
By default it is set to None.
by_group (bool) –
if True, store the data by group. Otherwise, store them by variables. Default: True
By default it is set to True.
categorize (bool) –
distinguish between the different groups of variables. Default: True.
By default it is set to True.
inputs_names (list(str)) –
list of inputs names. If None, use all inputs. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
outputs_names (list(str)) –
list of outputs names. If None, use all outputs. Default: None.
By default it is set to None.
- export_to_ggobi(file_path, inputs_names=None, outputs_names=None)
Export history to xml file format for ggobi tool.
- Parameters
file_path (str) – Path to export the file.
inputs_names (list(str)) –
List of inputs to include in the export. By default, take all of them.
By default it is set to None.
outputs_names (list(str)) –
Names of outputs to export. By default, take all of them.
By default it is set to None.
- get_all_data(as_iterator=False)
Return all the data in the cache.
- Parameters
as_iterator (bool) –
If True, return an iterator. Otherwise a dictionary. Default: False.
By default it is set to False.
- Returns
all_data – A dictionary of dictionaries for inputs, outputs and jacobian where keys are data indices.
- Return type
dict
- get_data(index, **options)[source]
Gets the data associated to a sample ID.
- Parameters
index (str) – sample ID.
options – options passed to the _read_data() method.
- Returns
input data, output data and jacobian.
- Return type
dict
- get_last_cached_inputs()
Retrieve the last execution inputs.
- Returns
inputs – Last cached inputs.
- Return type
dict
- get_last_cached_outputs()
Retrieve the last execution outputs.
- Returns
outputs – Last cached outputs.
- Return type
dict
- get_length()
Get the length of the cache, ie the number of stored elements.
- Returns
length – Length of the cache.
- Return type
int
- get_outputs(input_data, input_names=None)
Check if the discipline has already been evaluated for the given input data dictionary. If True, return the associated cache, otherwise return None.
- Parameters
input_data (dict) – Input data dictionary to test for caching.
input_names (list(str)) –
List of input data names.
By default it is set to None.
- Returns
output_data (dict) – Output data if there is no need to evaluate the discipline. None otherwise.
jacobian (dict) – Jacobian if there is no need to evaluate the discipline. None otherwise.
- property inputs_names
Return the inputs names.
- property max_length
Get the maximal length of the cache (the maximal number of stored elements).
- Returns
length – Maximal length of the cache.
- Return type
int
- merge(other_cache)
Merges an other cache with self.
- Parameters
other_cache (AbstractFullCache) – Cache to merge with the current one.
- property outputs_names
Return the outputs names.
- property samples_indices
List of samples indices.
- static update_file_format(hdf_file_path)[source]
Update the format of a HDF5 file.
See also
- Parameters
hdf_file_path (Union[str, pathlib.Path]) – A HDF5 file path.
- Return type
None
- property varsizes
Return the variables sizes.
[DEV] The abstract caches¶
MemoryFullCacheandHDF5Cacheinherit fromAbstractFullCache.AbstractFullCacheandSimpleCacheinherit fromAbstractCache.Both
AbstractCacheandAbstractFullCacheare abstract classes.Any class inheriting from
AbstractCachecan be instantiated from theCacheFactory.
