Note
Click here to download the full example code
Machine learning algorithm selection example¶
In this example we use the MLAlgoSelection class to perform a grid
search over different algorithms and hyperparameter values.
from __future__ import annotations
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from gemseo.algos.design_space import DesignSpace
from gemseo.core.dataset import Dataset
from gemseo.mlearning.core.selection import MLAlgoSelection
from gemseo.mlearning.qual_measure.mse_measure import MSEMeasure
np.random.seed(54321)
Build dataset¶
The data consists of a 1D-function \(f:[0,1]\to[0,1]\), where \(f(x)=x^2\). The inputs \((x_i)_{i=1,\cdots,n}\) are chosen randomly from the interval \([0,1]\). The outputs \(y_i = f(x_i) + \epsilon_i`contain added noise, where :math:\)epsilon_itilde mathcal{N}(0,sigma^2)`. We choose \(n=20\) and \(\sigma=0.05\).
n = 20
x = np.sort(np.random.random(n))
y = x**2 + np.random.normal(0, 0.05, n)
dataset = Dataset()
dataset.add_variable("x", x[:, None], Dataset.INPUT_GROUP)
dataset.add_variable("y", y[:, None], Dataset.OUTPUT_GROUP, cache_as_input=False)
Build selector¶
We consider three regression models, with different possible hyperparameters. A mean squared error quality measure is used with a k-folds cross validation scheme (5 folds).
selector = MLAlgoSelection(dataset, MSEMeasure, eval_method="kfolds", n_folds=5)
selector.add_candidate(
"LinearRegressor",
penalty_level=[0, 0.1, 1, 10, 20],
l2_penalty_ratio=[0, 0.5, 1],
fit_intercept=[True],
)
selector.add_candidate(
"PolynomialRegressor",
degree=[2, 3, 4, 10],
penalty_level=[0, 0.1, 1, 10],
l2_penalty_ratio=[1],
fit_intercept=[True, False],
)
rbf_space = DesignSpace()
rbf_space.add_variable("epsilon", 1, "float", 0.01, 0.1, 0.05)
selector.add_candidate(
"RBFRegressor",
calib_space=rbf_space,
calib_algo={"algo": "fullfact", "n_samples": 16},
smooth=[0, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100],
)
Select best candidate¶
best_algo = selector.select()
print(best_algo)
PolynomialRegressor(degree=2, fit_intercept=False, l2_penalty_ratio=1, penalty_level=0)
based on the scikit-learn library
built from 20 learning samples
Plot results¶
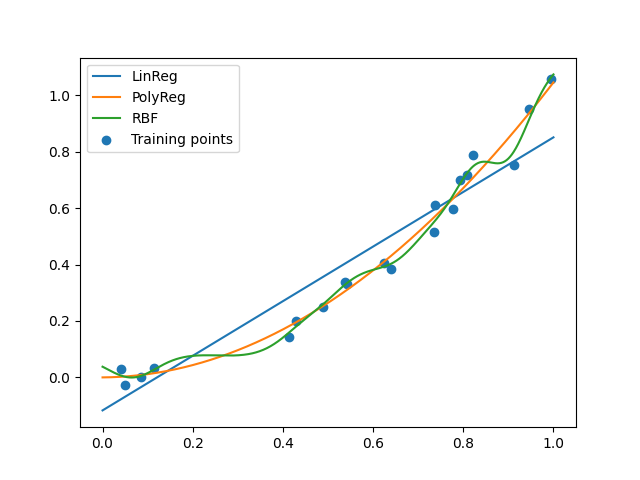
Plot the best models from each candidate algorithm
finex = np.linspace(0, 1, 1000)
for candidate in selector.candidates:
algo = candidate[0]
print(algo)
predy = algo.predict(finex[:, None])[:, 0]
plt.plot(finex, predy, label=algo.SHORT_ALGO_NAME)
plt.scatter(x, y, label="Training points")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
LinearRegressor(fit_intercept=True, l2_penalty_ratio=1, penalty_level=0.1)
based on the scikit-learn library
built from 20 learning samples
PolynomialRegressor(degree=2, fit_intercept=False, l2_penalty_ratio=1, penalty_level=0)
based on the scikit-learn library
built from 20 learning samples
RBFRegressor(epsilon=0.1, function=multiquadric, norm=euclidean, smooth=0.01)
based on the SciPy library
built from 20 learning samples
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.971 seconds)
