rbf module¶
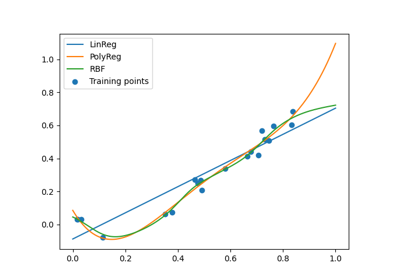
The RBF network for regression.
The radial basis function surrogate discipline expresses the model output as a weighted sum of kernel functions centered on the learning input data:
and the coefficients \((w_1, w_2, \ldots, w_n)\) are estimated by least squares minimization.
Dependence¶
The RBF model relies on the Rbf class of the scipy library.
- class gemseo.mlearning.regression.rbf.RBFRegressor(data, transformer=mappingproxy({}), input_names=None, output_names=None, function=Function.MULTIQUADRIC, der_function=None, epsilon=None, smooth=0.0, norm='euclidean')[source]¶
Bases:
BaseMLRegressionAlgoRegression based on radial basis functions (RBFs).
This model relies on the SciPy class
scipy.interpolate.Rbf.- Parameters:
data (IODataset) – The learning dataset.
transformer (TransformerType) –
The strategies to transform the variables. The values are instances of
BaseTransformerwhile the keys are the names of either the variables or the groups of variables, e.g."inputs"or"outputs"in the case of the regression algorithms. If a group is specified, theBaseTransformerwill be applied to all the variables of this group. IfIDENTITY, do not transform the variables.By default it is set to {}.
input_names (Iterable[str] | None) – The names of the input variables. If
None, consider all the input variables of the learning dataset.output_names (Iterable[str] | None) – The names of the output variables. If
None, consider all the output variables of the learning dataset.function (Function | Callable[[float, float], float]) –
The radial basis function taking a radius \(r\) as input, representing a distance between two points. If it is a string, then it must be one of the following:
"multiquadric"for \(\sqrt{(r/\epsilon)^2 + 1}\),"inverse"for \(1/\sqrt{(r/\epsilon)^2 + 1}\),"gaussian"for \(\exp(-(r/\epsilon)^2)\),"linear"for \(r\),"cubic"for \(r^3\),"quintic"for \(r^5\),"thin_plate"for \(r^2\log(r)\).
If it is a callable, then it must take the two arguments
selfandras inputs, e.g.lambda self, r: sqrt((r/self.epsilon)**2 + 1)for the multiquadric function. The epsilon parameter will be available asself.epsilon. Other keyword arguments passed in will be available as well.By default it is set to “multiquadric”.
der_function (Callable[[RealArray], RealArray] | None) – The derivative of the radial basis function, only to be provided if
functionis a callable and if the use of the model with its derivative is required. IfNoneand iffunctionis a callable, an error will be raised. IfNoneand iffunctionis a string, the class will look for its internal implementation and will raise an error if it is missing. Theder_functionshall take three arguments (input_data,norm_input_data,eps). For an RBF of the form function(\(r\)), der_function(\(x\), \(|x|\), \(\epsilon\)) shall return \(\epsilon^{-1} x/|x| f'(|x|/\epsilon)\).epsilon (float | None) – An adjustable constant for Gaussian or multiquadric functions. If
None, use the average distance between input data.smooth (float) –
The degree of smoothness,
0involving an interpolation of the learning points.By default it is set to 0.0.
norm (str | Callable[[RealArray, RealArray], float]) –
The distance metric to be used, either a distance function name known by SciPy or a function that computes the distance between two points.
By default it is set to “euclidean”.
- Raises:
ValueError – When both the variable and the group it belongs to have a transformer.
- DataFormatters¶
alias of
RegressionDataFormatters
- class Function(value)[source]¶
Bases:
StrEnumThe radial basis functions.
- CUBIC = 'cubic'¶
- GAUSSIAN = 'gaussian'¶
- INVERSE_MULTIQUADRIC = 'inverse_multiquadric'¶
- LINEAR = 'linear'¶
- MULTIQUADRIC = 'multiquadric'¶
- QUINTIC = 'quintic'¶
- THIN_PLATE = 'thin_plate'¶
- class RBFDerivatives[source]¶
Bases:
objectDerivatives of functions used in
RBFRegressor.For an RBF of the form \(f(r)\), \(r\) scalar, the derivative functions are defined by \(d(f(r))/dx\), with \(r=|x|/\epsilon\). The functions are thus defined by \(df/dx = \epsilon^{-1} x/|x| f'(|x|/\epsilon)\). This convention is chosen to avoid division by \(|x|\) when the terms may be cancelled out, as \(f'(r)\) often has a term in \(r\).
- classmethod der_cubic(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative w.r.t. \(x\) of the function \(f(r) = r^3\).
- classmethod der_gaussian(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative of \(f(r)=\exp(-r^2)\) w.r.t. \(x\).
- classmethod der_inverse_multiquadric(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative of \(f(r)=1/\sqrt{r^2 + 1}\) w.r.t. \(x\).
- classmethod der_linear(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative of \(f(r)=r\) w.r.t. \(x\).
If \(x=0\), return 0 (determined up to a tolerance).
- classmethod der_multiquadric(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative of \(f(r) = \sqrt{r^2 + 1}\) w.r.t. \(x\).
- classmethod der_quintic(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative w.r.t. \(x\) of the function \(f(r) = r^5\).
- classmethod der_thin_plate(input_data, norm_input_data, eps)[source]¶
Compute derivative of \(f(r) = r^2\log(r)\) w.r.t. \(x\).
If \(x=0\), return 0 (determined up to a tolerance).
- TOL = 2.220446049250313e-16¶
- learn(samples=None, fit_transformers=True)¶
Train the machine learning algorithm from the learning dataset.
- load_algo(directory)¶
Load a machine learning algorithm from a directory.
- Parameters:
directory (str | Path) – The path to the directory where the machine learning algorithm is saved.
- Return type:
None
- predict(input_data)¶
Predict output data from input data.
The user can specify these input data either as a NumPy array, e.g.
array([1., 2., 3.])or as a dictionary, e.g.{'a': array([1.]), 'b': array([2., 3.])}.If the numpy arrays are of dimension 2, their i-th rows represent the input data of the i-th sample; while if the numpy arrays are of dimension 1, there is a single sample.
The type of the output data and the dimension of the output arrays will be consistent with the type of the input data and the size of the input arrays.
- predict_jacobian(input_data)¶
Predict the Jacobians of the regression model at input_data.
The user can specify these input data either as a NumPy array, e.g.
array([1., 2., 3.])or as a dictionary, e.g.{'a': array([1.]), 'b': array([2., 3.])}.If the NumPy arrays are of dimension 2, their i-th rows represent the input data of the i-th sample; while if the NumPy arrays are of dimension 1, there is a single sample.
The type of the output data and the dimension of the output arrays will be consistent with the type of the input data and the size of the input arrays.
- Parameters:
input_data (DataType) – The input data.
- Returns:
The predicted Jacobian data.
- Return type:
NoReturn
- predict_raw(input_data)¶
Predict output data from input data.
- Parameters:
input_data (RealArray) – The input data with shape (n_samples, n_inputs).
- Returns:
The predicted output data with shape (n_samples, n_outputs).
- Return type:
RealArray
- to_pickle(directory=None, path='.', save_learning_set=False)¶
Save the machine learning algorithm.
- Parameters:
directory (str | None) – The name of the directory to save the algorithm.
path (str | Path) –
The path to parent directory where to create the directory.
By default it is set to “.”.
save_learning_set (bool) –
Whether to save the learning set or get rid of it to lighten the saved files.
By default it is set to False.
- Returns:
The path to the directory where the algorithm is saved.
- Return type:
- DEFAULT_TRANSFORMER: DefaultTransformerType = mappingproxy({'inputs': <gemseo.mlearning.transformers.scaler.min_max_scaler.MinMaxScaler object>, 'outputs': <gemseo.mlearning.transformers.scaler.min_max_scaler.MinMaxScaler object>})¶
The default transformer for the input and output data, if any.
- IDENTITY: Final[DefaultTransformerType] = mappingproxy({})¶
A transformer leaving the input and output variables as they are.
- LIBRARY: ClassVar[str] = 'SciPy'¶
The name of the library of the wrapped machine learning algorithm.
- SHORT_ALGO_NAME: ClassVar[str] = 'RBF'¶
The short name of the machine learning algorithm, often an acronym.
Typically used for composite names, e.g.
f"{algo.SHORT_ALGO_NAME}_{dataset.name}"orf"{algo.SHORT_ALGO_NAME}_{discipline.name}".
- algo: Any¶
The interfaced machine learning algorithm.
- der_function: Callable[[RealArray], RealArray]¶
The derivative of the radial basis function.
- property function: str¶
The name of the kernel function.
The name is possibly different from self.parameters[‘function’], as it is mapped (scipy). Examples:
‘inverse’ -> ‘inverse_multiquadric’ ‘InverSE MULtiQuadRIC’ -> ‘inverse_multiquadric’
- property learning_samples_indices: Sequence[int]¶
The indices of the learning samples used for the training.
- resampling_results: dict[str, tuple[BaseResampler, list[BaseMLAlgo], list[ndarray] | ndarray]]¶
The resampler class names bound to the resampling results.
A resampling result is formatted as
(resampler, ml_algos, predictions)whereresampleris aBaseResampler,ml_algosis the list of the associated machine learning algorithms built during the resampling stage andpredictionsare the predictions obtained with the latter.resampling_resultsstores only one resampling result per resampler type (e.g.,"CrossValidation","LeaveOneOut"and"Boostrap").
- transformer: dict[str, BaseTransformer]¶
The strategies to transform the variables, if any.
The values are instances of
BaseTransformerwhile the keys are the names of either the variables or the groups of variables, e.g. “inputs” or “outputs” in the case of the regression algorithms. If a group is specified, theBaseTransformerwill be applied to all the variables of this group.
- y_average: RealArray¶
The mean of the learning output data.