Optimization and DOE framework¶
In this section we describe GEMSEO’s optimization and DOE framework.
The standard way to use GEMSEO is through an MDOScenario, which
automatically creates an OptimizationProblem from a MDO formulation and a set of MDODiscipline.
However, one may be interested in directly creating an OptimizationProblem using the class OptimizationProblem,
which can be solved using an optimization algorithm or sampled with a DOE algorithm.
Warning
MDO formulation and optimization problem developers should also understand this part of GEMSEO.
Setting up an OptimizationProblem¶
The OptimizationProblem class is composed of at least a
DesignSpace created from create_design_space() which describes the design variables:
from gemseo. api import create_design_space
from numpy import ones
design_space = create_design_space()
design_space.add_variable("x", 1, l_b=-2., u_b=2.,
value=-0.5 * np.ones(1))
and an objective function, of type MDOFunction. The MDOFunction is callable and requires at least
a function pointer to be instantiated. It supports expressions and the +, -, * operators:
from gemseo.algos import MDOFunction
f_1 = MDOFunction(np.sin, name="f_1", jac=np.cos, expr="sin(x)")
f_2 = MDOFunction(np.exp, name="f_2", jac=np.exp, expr="exp(x)")
f_1_sub_f_2 = f_1 - f_2
From this DesignSpace, an OptimizationProblem is built:
from gemseo.algos import OptimizationProblem, MDOFunction,
problem = OptimizationProblem(design_space)
To set the objective MDOFunction, the attribute OptimizationProblem.objective of class OptimizationProblem
must be set with the objective function pointer:
problem.objective = f_1_sub_f_2
Similarly the OptimizationProblem.constraints attribute must be set with a list of inequality or equality constraints.
The MDOFunction.f_type attribute of MDOFunction shall be set to "eq" or "ineq" to declare the type of constraint to equality or inequality.
Warning
All inequality constraints must be negative by convention, whatever the optimization algorithm used to solve the problem.
Solving the problem by optimization¶
Once the optimization problem created, it can be solved using one of the available
optimization algorithms from the OptimizersFactory,
by means of the function .OptimizersFactory.execute()
whose mandatory arguments are the OptimizationProblem
and the optimization algorithm name. For example, in the case of the L-BFGS-B algorithm
with normalized design space, we have:
from gemseo.algos import OptimizersFactory
opt = OptimizersFactory().execute(problem, "L-BFGS-B",
normalize_design_space=True)
print "Optimum = " + str(opt)
Note that the L-BFGS-B algorithm is implemented in the external
library SciPy
and interfaced with GEMSEO through the class ScipyOpt.
The list of available algorithms depend on the local setup of GEMSEO, and the installed optimization libraries. It can be obtained using :
algo_list = OptimizersFactory().algorithms
print(f"Available algorithms: {algo_list}")
The optimization history can be saved to the disk for further analysis,
without having to re execute the optimization.
For that, we use the function OptimizationProblem.to_hdf():
problem.to_hdf("simple_opt.hdf5")
Solving the problem by DOE¶
DOE algorithms can also be used to sample the design space and observe the value of the objective and constraints
from gemseo.algos import DOEFactory
# And solve it with |g| interface
opt = DOEFactory().execute(problem, "lhs", n_samples=10,
normalize_design_space=True)
Results analysis¶
The optimization history can be plotted using one of the post processing tools, see the post-processing page.
from gemseo import execute_post
execute_post(problem, "OptHistoryView", save=True, file_path="simple_opt")
# Also works from disk
execute_post("my_optim.hdf5", "OptHistoryView", save=True, file_path="opt_view_from_disk")
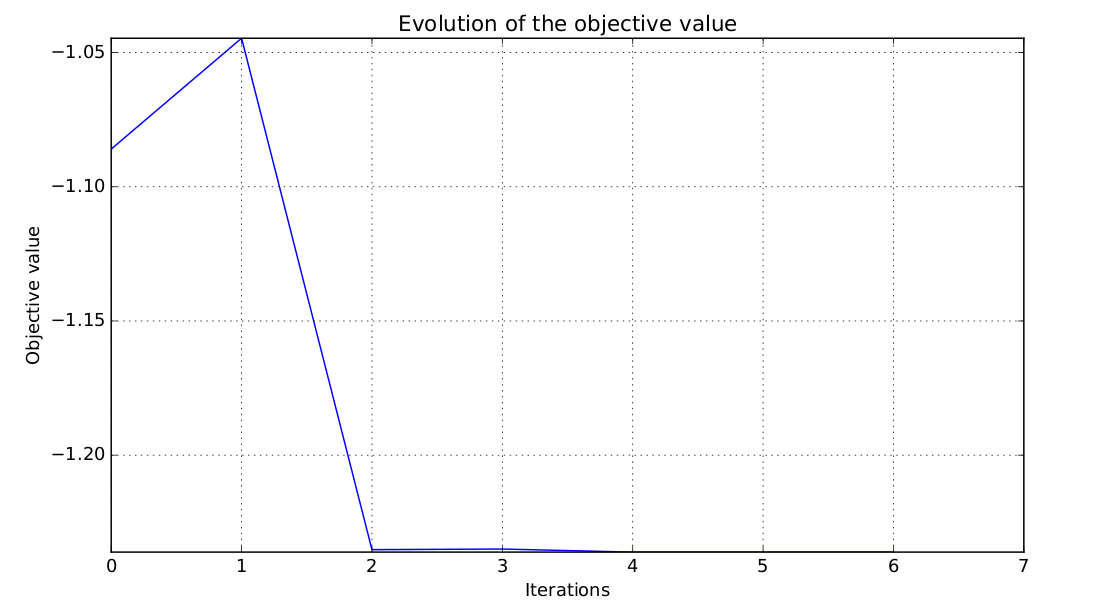
Objective function history for the simple analytic optimization¶
DOE algorithms¶
GEMSEO is interfaced with two packages that provide DOE algorithms:
pyDOE, and
OpenTURNS.
To list the available DOE algorithms in the current GEMSEO configuration, use
gemseo.get_available_doe_algorithms().
The set of plots below shows plots using various available algorithms.
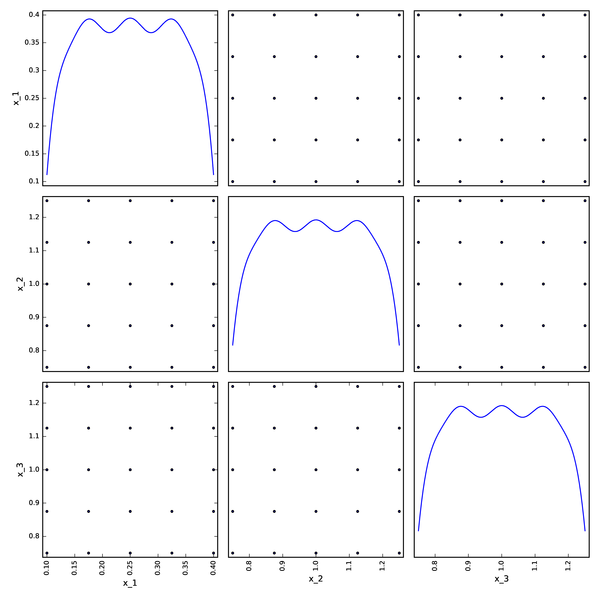
Full factorial DOE from pyDOE¶
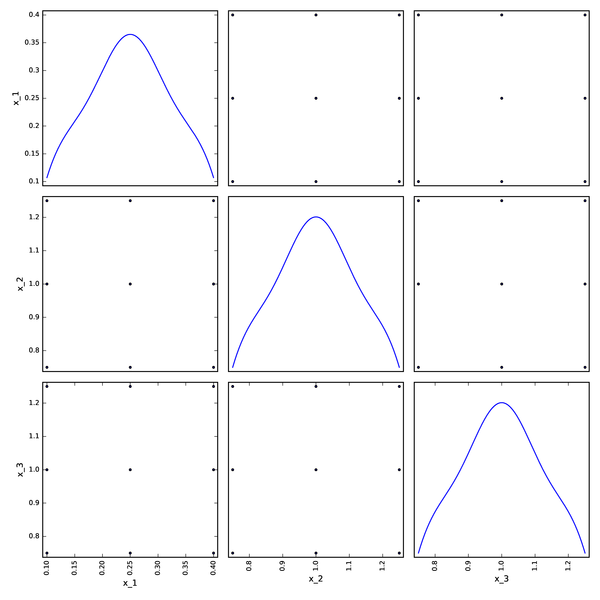
Box-Behnken DOE from pyDOE¶
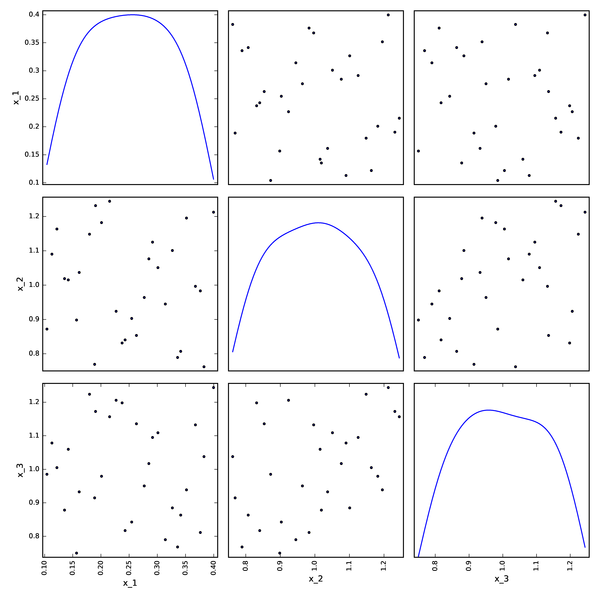
LHS DOE from pyDOE¶
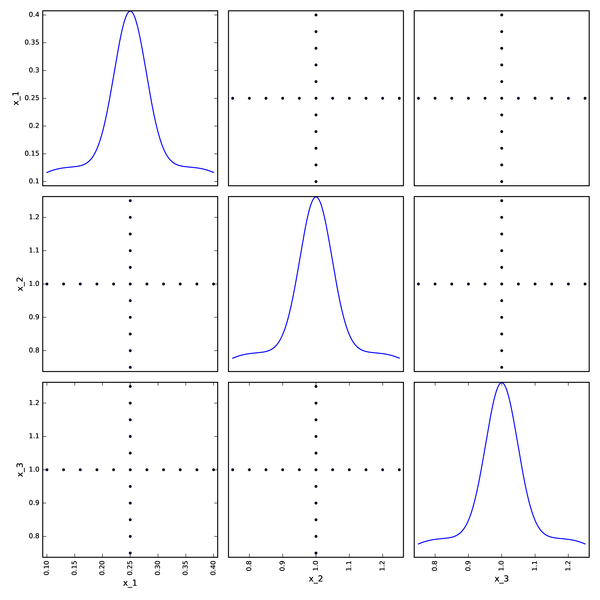
Axial DOE from OpenTURNS¶
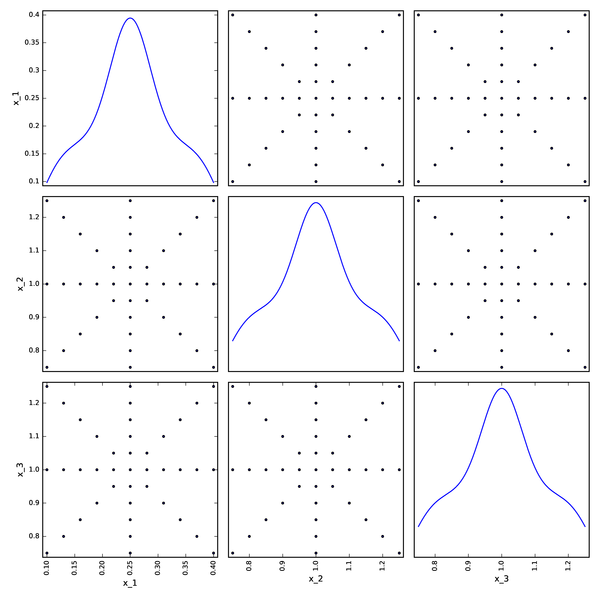
Composite DOE from OpenTURNS¶
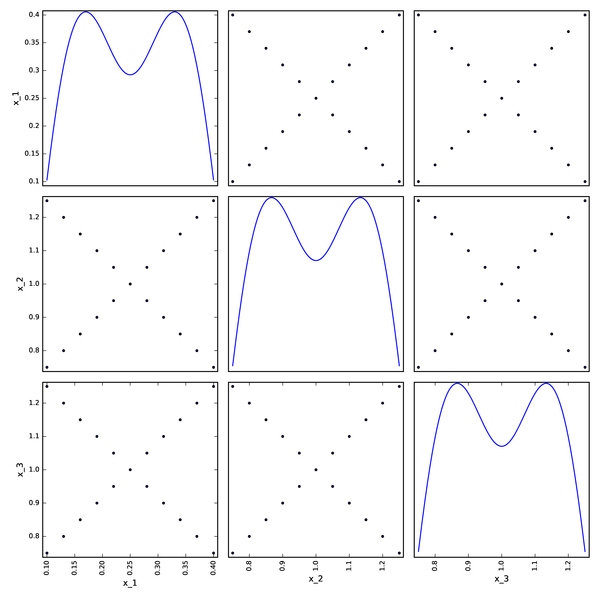
Full Factorial DOE from OpenTURNS¶
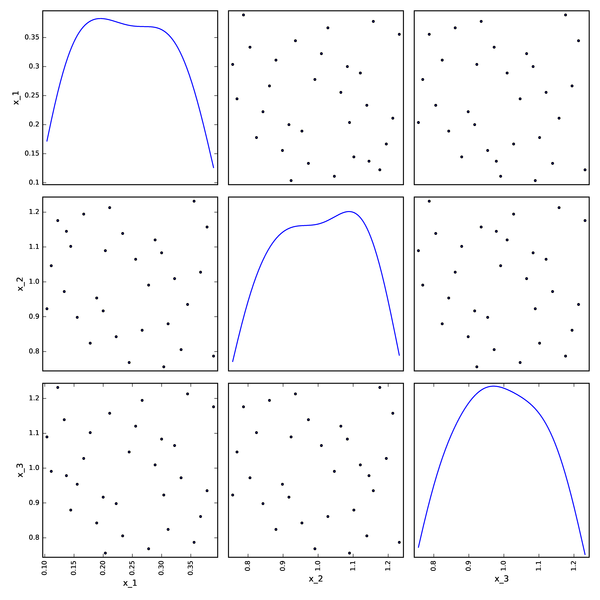
Faure DOE from OpenTURNS¶
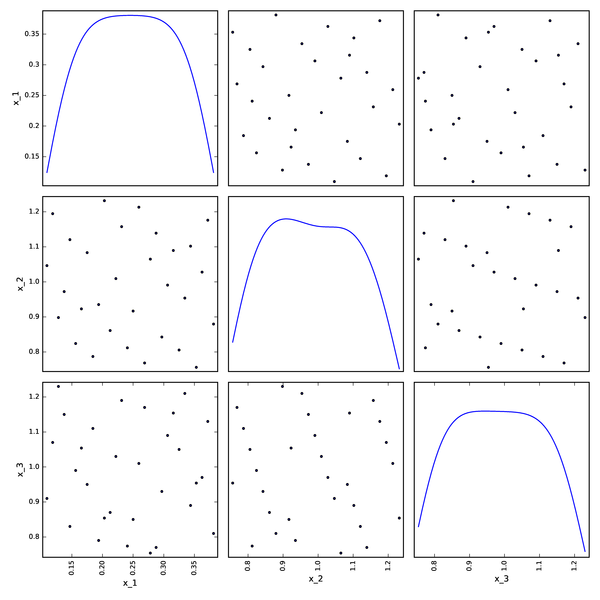
Halton DOE from OpenTURNS¶
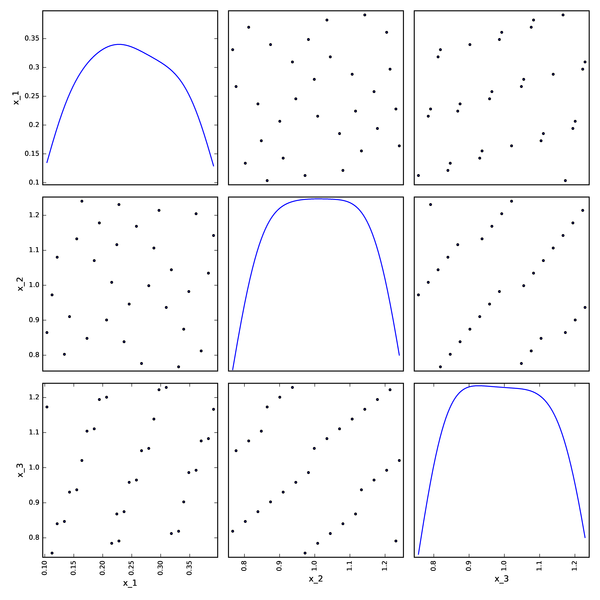
Haselgrove DOE from OpenTURNS¶
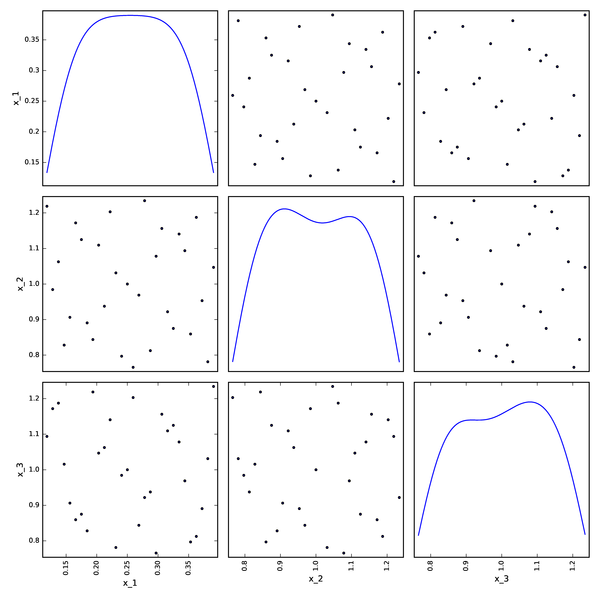
Sobol DOE from OpenTURNS¶
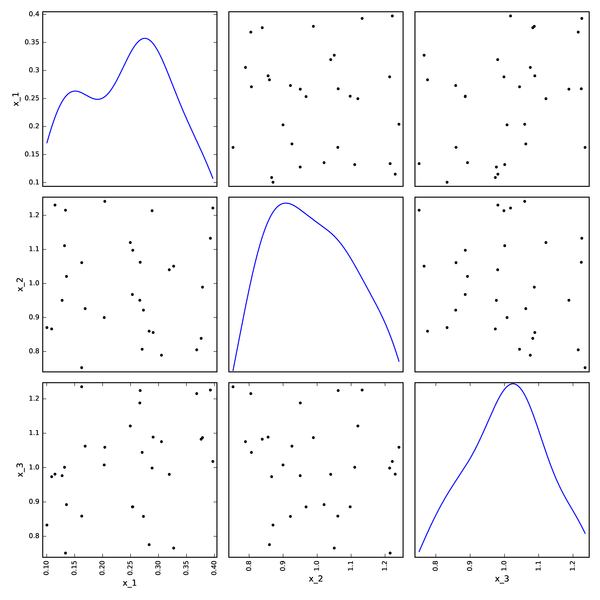
Monte-Carlo DOE from OpenTURNS¶
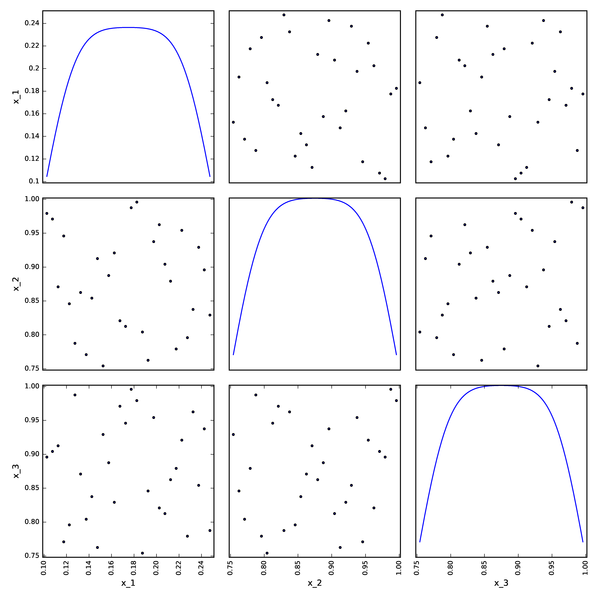
LHSC DOE from OpenTURNS¶
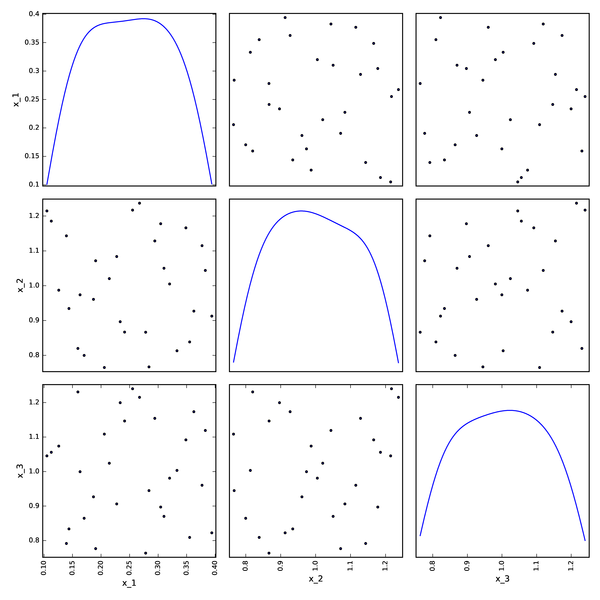
LHS DOE from OpenTURNS¶
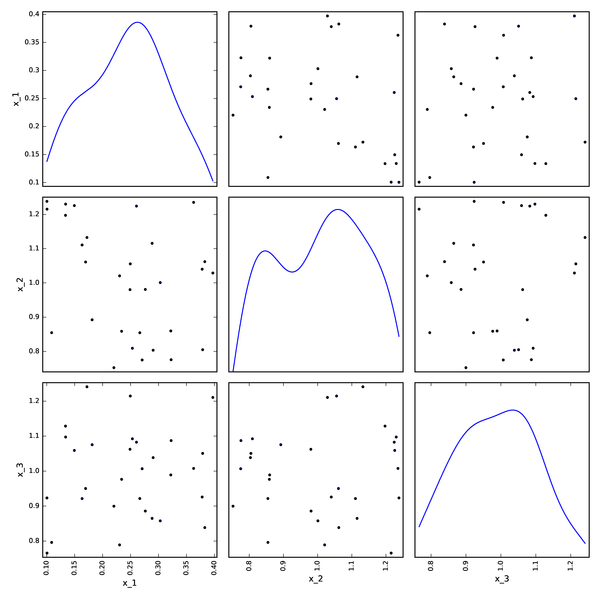
Random DOE from OpenTURNS¶
