design_space module¶
Design space.
A design space is used to represent the optimization’s unknowns, a.k.a. design variables.
A DesignSpace describes this design space at a given state,
in terms of names, sizes, types, bounds and current values of the design variables.
Variables can easily be added to the DesignSpace
using the DesignSpace.add_variable() method
or removed using the DesignSpace.remove_variable() method.
We can also filter the design variables using the DesignSpace.filter() method.
Getters and setters are also available to get or set the value of a given variable property.
Lastly,
an instance of DesignSpace can be stored in a txt or HDF file.
- class gemseo.algos.design_space.DesignSpace(hdf_file=None, name=None)[source]¶
Bases:
MutableMappingDescription of a design space.
It defines a set of variables from their names, sizes, types and bounds.
In addition, it provides the current values of these variables that can be used as the initial solution of an
OptimizationProblem.A
DesignSpacehas the same API as a dictionary, e.g.variable = design_space["x"],other_design_space["x"] = design_space["x"],del design_space["x"],for name, value in design_space["x"].items(), …- Parameters:
- add_variable(name, size=1, var_type=DesignVariableType.FLOAT, l_b=None, u_b=None, value=None)[source]¶
Add a variable to the design space.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the variable.
size (int) –
The size of the variable.
By default it is set to 1.
var_type (VarType) –
Either the type of the variable or the types of its components.
By default it is set to FLOAT.
l_b (float | ndarray | None) – The lower bound of the variable. If None, use \(-\infty\).
u_b (float | ndarray | None) – The upper bound of the variable. If None, use \(+\infty\).
value (float | ndarray | None) – The default value of the variable. If None, do not use a default value.
- Raises:
ValueError – Either if the variable already exists or if the size is not a positive integer.
- Return type:
None
- array_to_dict(x_array)[source]¶
Convert a design array into a dictionary indexed by the variables names.
- Parameters:
x_array (ndarray) – A design value expressed as a NumPy array.
- Returns:
The design value expressed as a dictionary of NumPy arrays.
- Return type:
- check()[source]¶
Check the state of the design space.
- Raises:
ValueError – If the design space is empty.
- Return type:
None
- check_membership(x_vect, variable_names=None)[source]¶
Check whether the variables satisfy the design space requirements.
- Parameters:
- Raises:
ValueError – Either if the dimension of the values vector is wrong, if the values are not specified as an array or a dictionary, if the values are outside the bounds of the variables or if the component of an integer variable is not an integer.
- Return type:
None
- clear() None. Remove all items from D.¶
- dict_to_array(design_values, variable_names=None)[source]¶
Convert a point as dictionary into an array.
- export_to_txt(output_file, fields=None, header_char='', **table_options)[source]¶
Export the design space to a text file.
- Parameters:
output_file (str | Path) – The path to the file.
fields (Sequence[str] | None) – The fields to be exported. If None, export all fields.
header_char (str) –
The header character.
By default it is set to “”.
**table_options (Any) – The names and values of additional attributes for the
PrettyTableview generated byDesignSpace.get_pretty_table().
- Return type:
None
- extend(other)[source]¶
Extend the design space with another design space.
- Parameters:
other (DesignSpace) – The design space to be appended to the current one.
- Return type:
None
- filter(keep_variables, copy=False)[source]¶
Filter the design space to keep a subset of variables.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
Either the filtered original design space or a copy.
- Raises:
ValueError – If the variable is not in the design space.
- Return type:
- filter_dim(variable, keep_dimensions)[source]¶
Filter the design space to keep a subset of dimensions for a variable.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The filtered design space.
- Raises:
ValueError – If a dimension is unknown.
- Return type:
- get(k[, d]) D[k] if k in D, else d. d defaults to None.¶
- get_active_bounds(x_vec=None, tol=1e-08)[source]¶
Determine which bound constraints of a design value are active.
- Parameters:
x_vec (ndarray | None) – The design value at which to check the bounds. If
None, use the current design value.tol (float) –
The tolerance of comparison of a scalar with a bound.
By default it is set to 1e-08.
- Returns:
Whether the components of the lower and upper bound constraints are active, the first returned value representing the lower bounds and the second one the upper bounds, e.g.
({'x': array(are_x_lower_bounds_active), 'y': array(are_y_lower_bounds_active)}, {'x': array(are_x_upper_bounds_active), 'y': array(are_y_upper_bounds_active)} )
where:
are_x_lower_bounds_active = [True, False] are_x_upper_bounds_active = [False, False] are_y_lower_bounds_active = [False] are_y_upper_bounds_active = [True]
- Return type:
- get_current_value(variable_names=None, complex_to_real=False, as_dict=False, normalize=False)[source]¶
Return the current design value.
If the names of the variables are empty then an empty data is returned.
- Parameters:
variable_names (Sequence[str] | None) – The names of the design variables. If
None, use all the design variables.complex_to_real (bool) –
Whether to cast complex numbers to real ones.
By default it is set to False.
as_dict (bool) –
Whether to return the current design value as a dictionary of the form
{variable_name: variable_value}.By default it is set to False.
normalize (bool) –
Whether to normalize the design values in \([0,1]\) with the bounds of the variables.
By default it is set to False.
- Returns:
The current design value.
- Raises:
ValueError – If names in
variable_namesare not in the design space.- Return type:
Warning
For performance purposes,
get_current_value()does not return a copy of the current value. This means that modifying the returned object will make theDesignSpaceinconsistent (the current design value stored as a NumPy array and the current design value stored as a dictionary of NumPy arrays will be different). To modify the returned object without impacting theDesignSpace, you shall copy this object and modify the copy.See also
To modify the current value, please use
set_current_value()orset_current_variable().
- get_indexed_var_name(variable_name)[source]¶
Create the names of the components of a variable.
If the size of the variable is equal to 1, this method returns the name of the variable. Otherwise, it concatenates the name of the variable, the separator
DesignSpace.SEPand the index of the component.
- get_indexed_variables_names()[source]¶
Create the names of the components of all the variables.
If the size of the variable is equal to 1, this method uses its name. Otherwise, it concatenates the name of the variable, the separator
DesignSpace.SEPand the index of the component.
- get_lower_bounds(variable_names=None)[source]¶
Generate an array of the variables’ lower bounds.
- Parameters:
variable_names (Sequence[str] | None) – The names of the variables of which the lower bounds are required. If None, use the variables of the design space.
- Returns:
The lower bounds of the variables.
- Return type:
ndarray
- get_pretty_table(fields=None, with_index=False)[source]¶
Build a tabular view of the design space.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
A tabular view of the design space.
- Return type:
- get_upper_bounds(variable_names=None)[source]¶
Generate an array of the variables’ upper bounds.
- Parameters:
variable_names (Sequence[str] | None) – The names of the variables of which the upper bounds are required. If None, use the variables of the design space.
- Returns:
The upper bounds of the variables.
- Return type:
ndarray
- get_variables_indexes(variable_names)[source]¶
Return the indexes of a design array corresponding to the variables names.
- has_current_value()[source]¶
Check if each variable has a current value.
- Returns:
Whether the current design value is defined for all variables.
- Return type:
- has_integer_variables()[source]¶
Check if the design space has at least one integer variable.
- Returns:
Whether the design space has at least one integer variable.
- Return type:
- import_hdf(file_path)[source]¶
Import a design space from an HDF file.
- Parameters:
file_path (str | Path) – The path to the file containing the description of a design space.
- Return type:
None
- initialize_missing_current_values()[source]¶
Initialize the current values of the design variables when missing.
Use:
the center of the design space when the lower and upper bounds are finite,
the lower bounds when the upper bounds are infinite,
the upper bounds when the lower bounds are infinite,
zero when the lower and upper bounds are infinite.
- Return type:
None
- items() a set-like object providing a view on D's items¶
- keys() a set-like object providing a view on D's keys¶
- normalize_grad(g_vect)[source]¶
Normalize an unnormalized gradient.
This method is based on the chain rule:
\[\frac{df(x)}{dx} = \frac{df(x)}{dx_u}\frac{dx_u}{dx} = \frac{df(x)}{dx_u}\frac{1}{u_b-l_b}\]where \(x_u = \frac{x-l_b}{u_b-l_b}\) is the normalized input vector, \(x\) is the unnormalized input vector and \(l_b\) and \(u_b\) are the lower and upper bounds of \(x\).
Then, the normalized gradient reads:
\[\frac{df(x)}{dx_u} = (u_b-l_b)\frac{df(x)}{dx}\]where \(\frac{df(x)}{dx}\) is the unnormalized one.
- normalize_vect(x_vect, minus_lb=True, out=None)[source]¶
Normalize a vector of the design space.
If minus_lb is True:
\[x_u = \frac{x-l_b}{u_b-l_b}\]where \(l_b\) and \(u_b\) are the lower and upper bounds of \(x\).
Otherwise:
\[x_u = \frac{x}{u_b-l_b}\]Unbounded variables are not normalized.
- Parameters:
x_vect (ndarray) – The values of the design variables.
minus_lb (bool) –
If True, remove the lower bounds at normalization.
By default it is set to True.
out (ndarray | None) – The array to store the normalized vector. If None, create a new array.
- Returns:
The normalized vector.
- Return type:
ndarray
- pop(k[, d]) v, remove specified key and return the corresponding value.¶
If key is not found, d is returned if given, otherwise KeyError is raised.
- popitem() (k, v), remove and return some (key, value) pair¶
as a 2-tuple; but raise KeyError if D is empty.
- project_into_bounds(x_c, normalized=False)[source]¶
Project a vector onto the bounds, using a simple coordinate wise approach.
- static read_from_txt(input_file, header=None)[source]¶
Create a design space from a text file.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
The design space read from the file.
- Raises:
ValueError – If the file does not contain the minimal variables in its header.
- Return type:
- remove_variable(name)[source]¶
Remove a variable from the design space.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the variable to be removed.
- Return type:
None
- set_current_value(value)[source]¶
Set the current design value.
- Parameters:
value (ndarray | Mapping[str, ndarray] | OptimizationResult) – The value of the current design.
- Raises:
ValueError – If the value has a wrong dimension.
TypeError – If the value is neither a mapping of NumPy arrays, a NumPy array nor an
OptimizationResult.
- Return type:
None
- set_lower_bound(name, lower_bound)[source]¶
Set the lower bound of a variable.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the variable.
lower_bound (ndarray | None) – The value of the lower bound.
- Raises:
ValueError – If the variable does not exist.
- Return type:
None
- set_upper_bound(name, upper_bound)[source]¶
Set the upper bound of a variable.
- Parameters:
name (str) – The name of the variable.
upper_bound (ndarray | None) – The value of the upper bound.
- Raises:
ValueError – If the variable does not exist.
- Return type:
None
- setdefault(k[, d]) D.get(k,d), also set D[k]=d if k not in D¶
- transform_vect(vector, out=None)[source]¶
Map a point of the design space to a vector with components in \([0,1]\).
- Parameters:
vector (ndarray) – A point of the design space.
out (ndarray | None) – The array to store the transformed vector. If None, create a new array.
- Returns:
A vector with components in \([0,1]\).
- Return type:
ndarray
- unnormalize_grad(g_vect)[source]¶
Unnormalize a normalized gradient.
This method is based on the chain rule:
\[\frac{df(x)}{dx} = \frac{df(x)}{dx_u}\frac{dx_u}{dx} = \frac{df(x)}{dx_u}\frac{1}{u_b-l_b}\]where \(x_u = \frac{x-l_b}{u_b-l_b}\) is the normalized input vector, \(x\) is the unnormalized input vector, \(\frac{df(x)}{dx_u}\) is the unnormalized gradient \(\frac{df(x)}{dx}\) is the normalized one, and \(l_b\) and \(u_b\) are the lower and upper bounds of \(x\).
- unnormalize_vect(x_vect, minus_lb=True, no_check=False, out=None)[source]¶
Unnormalize a normalized vector of the design space.
If minus_lb is True:
\[x = x_u(u_b-l_b) + l_b\]where \(x_u\) is the normalized input vector, \(x\) is the unnormalized input vector and \(l_b\) and \(u_b\) are the lower and upper bounds of \(x\).
Otherwise:
\[x = x_u(u_b-l_b)\]- Parameters:
x_vect (ndarray) – The values of the design variables.
minus_lb (bool) –
Whether to remove the lower bounds at normalization.
By default it is set to True.
no_check (bool) –
Whether to check if the components are in \([0,1]\).
By default it is set to False.
out (ndarray | None) – The array to store the unnormalized vector. If None, create a new array.
- Returns:
The unnormalized vector.
- Return type:
ndarray
- untransform_vect(vector, no_check=False, out=None)[source]¶
Map a vector with components in \([0,1]\) to the design space.
- Parameters:
vector (ndarray) – A vector with components in \([0,1]\).
no_check (bool) –
Whether to check if the components are in \([0,1]\).
By default it is set to False.
out (ndarray | None) – The array to store the untransformed vector. If None, create a new array.
- Returns:
A point of the variables space.
- Return type:
ndarray
- update([E, ]**F) None. Update D from mapping/iterable E and F.¶
If E present and has a .keys() method, does: for k in E: D[k] = E[k] If E present and lacks .keys() method, does: for (k, v) in E: D[k] = v In either case, this is followed by: for k, v in F.items(): D[k] = v
- values() an object providing a view on D's values¶
- AVAILABLE_TYPES = [<DesignVariableType.FLOAT: 'float'>, <DesignVariableType.INTEGER: 'integer'>]¶
- DESIGN_SPACE_GROUP = 'design_space'¶
- FLOAT = 'float'¶
- INTEGER = 'integer'¶
- LB_GROUP = 'l_b'¶
- MINIMAL_FIELDS = ['name', 'lower_bound', 'upper_bound']¶
- NAMES_GROUP = 'names'¶
- NAME_GROUP = 'name'¶
- SEP = '!'¶
- SIZE_GROUP = 'size'¶
- TABLE_NAMES = ['name', 'lower_bound', 'value', 'upper_bound', 'type']¶
- UB_GROUP = 'u_b'¶
- VALUE_GROUP = 'value'¶
- VAR_TYPE_GROUP = 'var_type'¶
- dimension: int¶
The total dimension of the space, corresponding to the sum of the sizes of the variables.
- class gemseo.algos.design_space.DesignVariable(size, var_type, l_b, u_b, value)¶
Bases:
tupleCreate new instance of DesignVariable(size, var_type, l_b, u_b, value)
- count(value, /)¶
Return number of occurrences of value.
- index(value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)¶
Return first index of value.
Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
- l_b¶
Alias for field number 2
- size¶
Alias for field number 0
- u_b¶
Alias for field number 3
- value¶
Alias for field number 4
- var_type¶
Alias for field number 1
- class gemseo.algos.design_space.DesignVariableType(value)[source]¶
Bases:
BaseEnumA type of design variable.
- FLOAT = 'float'¶
- INTEGER = 'integer'¶
Examples using DesignSpace¶
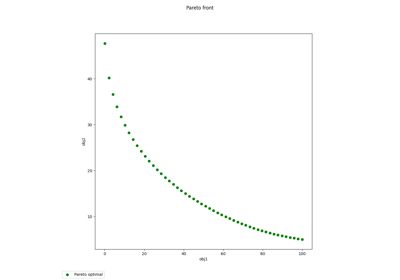
Pareto front on Binh and Korn problem using a BiLevel formulation
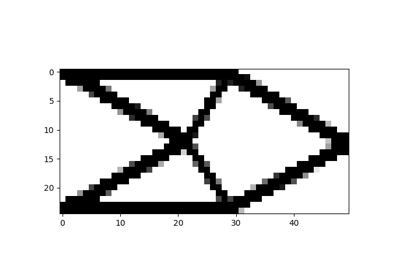
Solve a 2D short cantilever topology optimization problem
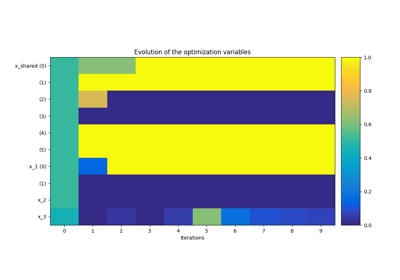
Application: Sobieski’s Super-Sonic Business Jet (MDO)

MDO formulations for a toy example in aerostructure
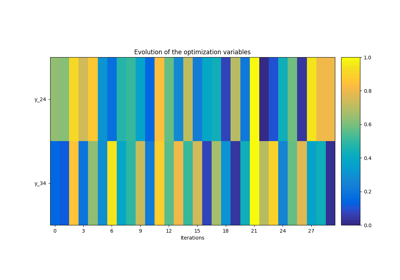
Simple disciplinary DOE example on the Sobieski SSBJ test case